Nutraceuticals: Pharmacologically Active Potent Dietary Supplements
- PMID: 35832855
- PMCID: PMC9273442
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2051017
Nutraceuticals: Pharmacologically Active Potent Dietary Supplements
Abstract
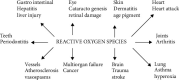
A growing demand exists for nutraceuticals, which seem to reside in the grey area between pharmaceuticals and food. Nutraceuticals, up today, do not have a specific definition distinct from those of other food-derived categories, e.g., food supplements, herbal products, functional foods, and fortified foods. They have, however, a pharmacological beneficial effect on health. Many studies have been recently addressed to assess their safety, efficacy, and regulation. The object of writing this review article is that we need to pay more attention to natural and organic foods. The bases of nutraceutical components (food supplements) are known for potent and powerful clinical evidence effects on the treatment of hypertension and type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2022 Subhash Chandra et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any warfare of hobby or monetary or any other case.
Figures
References
-
- Daliu P., Santini A., Novellino E. From pharmaceuticals to nutraceuticals: bridging disease prevention and management. Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology . 2019;12:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Berger M. M., Spertin F., Shenkin A. Clinical Immune and metabolic effects of trace element supplements in burns, a double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Clinical Nutrition . 1996;15(2):94–96. - PubMed
-
- Ramaa C. S., Shirode A. R., Mundada A. S. Nutraceuticals- an emerging era in the treatment and prevention of cardiovascular diseases. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology . 2006;7:15–23. - PubMed
-
- Bagchi D., Preuss H. G. Nutraceutical and functional food industries, aspects on safety and regulatory requirements. Toxicology Letters . 2004;1(150):1–2.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical