Global Research Trends in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Bibliometric and Visualized Study
- PMID: 35833106
- PMCID: PMC9271748
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.922063
Global Research Trends in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Bibliometric and Visualized Study
Abstract
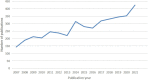
Background: There are about 10-23% of adults worldwide suffering from irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Over the past few decades, there are many aspects of uncertainty regarding IBS leading to an ongoing interest in the topic as reflected by a vast number of publications, whose heterogeneity and variable quality may challenge researchers to measure their scientific impact, to identify collaborative networks, and to grasp actively researched themes. Accordingly, with help from bibliometric approaches, our goal is to assess the structure, evolution, and trends of IBS research between 2007 and 2022.
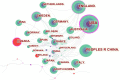
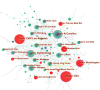
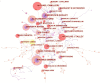
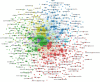
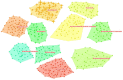
Methods: The documents exclusively focusing on IBS from 2007 to 2022 were retrieved from the Science Citation Index Expanded of the Web of Science Core Collection. The annual productivity of IBS research, and the most prolific countries or regions, authors, journals and resource-, intellectual- and knowledge-sharing in IBS research, as well as co-citation analysis of references and keywords were analyzed through Microsoft Office Excel 2019, CiteSpace, and VOSviewer.
Results: In total, 4,092 publications were reviewed. The USA led the list of countries with the most publications (1,226, 29.96%). Mayo Clinic contributed more publications than any other institution (193, 4.71%). MAGNUS SIMREN stood out as the most active and impactful scholar with the highest number of publications and the greatest betweenness centrality value. The most high-yield journal in this field was Neurogastroenterology and motility: the official journal of the European Gastrointestinal Motility Society (275, 6.72%). Gastroenterology had the most co-citations (3,721, 3.60%). Keywords with the ongoing strong citation bursts were chromogranin A, rat model, peptide YY, gut microbiota, and low-FODMAP diet, etc.
Conclusion: Through bibliometric analysis, we gleaned deep insight into the current status of literature investigating IBS for the first time. These findings will be useful to scholars interested in understanding the key information in the field, as well as identifying possible research frontiers.
Keywords: CiteSpace; VOSviewer; bibliometrics; hot topics; irritable bowel syndrome; trends.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Ma, Tian, Zhang, Wei, Zhang, Wang and Tang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Trends in gastroesophageal reflux disease research: A bibliometric and visualized study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 29;9:994534. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.994534. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36250094 Free PMC article.
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
Bibliometric analysis of the 100 most-cited papers about the role of gut microbiota in irritable bowel syndrome from 2000 to 2021.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Oct;23(6):2759-2772. doi: 10.1007/s10238-022-00971-5. Epub 2022 Dec 15. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 36522553
-
Research trends in the field of the gut-brain interaction: Functional dyspepsia in the spotlight - An integrated bibliometric and science mapping approach.Front Neurosci. 2023 Mar 8;17:1109510. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1109510. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36968499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global research progress of visceral hypersensitivity and irritable bowel syndrome: bibliometrics and visualized analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 May 2;14:1175057. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1175057. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37201020 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Psychological determinants of irritable bowel syndrome and its impact on quality of life: a machine learning approaches.Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2025;18(1):100-114. doi: 10.22037/ghfbb.v18i1.3082. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2025. PMID: 40734808 Free PMC article.
-
The gut microbiota metabolite butyrate mitigates MPTP/MPP+ -induced Parkinson's disease by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2023 Oct;39(10):1002-1010. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12745. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37807941 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in gastroesophageal reflux disease research: A bibliometric and visualized study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 29;9:994534. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.994534. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36250094 Free PMC article.
-
Sentiment analysis and topic modeling of social media data to explore public discourse on irritable bowel syndrome.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21550. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08599-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40596686 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping knowledge landscapes and emerging trends of sonodynamic therapy: A bibliometric and visualized study.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 9;13:1048211. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1048211. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36699067 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

