Immune Responses Against SARS-CoV-2 WT and Delta Variant in Elderly BNT162b2 Vaccinees
- PMID: 35833113
- PMCID: PMC9271971
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.868361
Immune Responses Against SARS-CoV-2 WT and Delta Variant in Elderly BNT162b2 Vaccinees
Abstract
Background: Residents of nursing homes are one of the most vulnerable groups during the severe acute syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic. The aim of this study was to characterize cellular and humoral immune responses in >70-year-old participants before vaccination, after first and second vaccination with BNT162b2, in contrast to second-dose-vaccinated participants younger than 60 years.
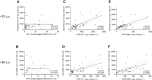
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells of 45 elderly and 40 younger vaccinees were analyzed by IFNγ ELISpot, specific immunoglobulin G antibody titers against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, and neutralization abilities against SARS-CoV-2 wild-type (WT) and Delta variant (B.1.617.2).
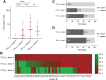
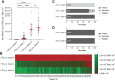
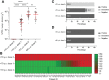
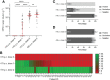
Results: Our results clearly demonstrate a significantly increased T cell response, IgG titers, and neutralization activities against SARS-CoV-2 WT and Delta between first and second vaccination with BNT162b2 in elderly vaccinees, thereby highlighting the importance of the second booster. Interestingly, similar cellular and humoral immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 WT and Delta were found after the second vaccine dose in the young and elderly groups.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate a full picture of cellular and humoral immune responses of BNT162b2-vaccinees in two age cohorts. In all vaccines, SARS-CoV-2 WT-specific antibodies with similar neutralizing activity were detected in all vaccinees. After the second vaccination, neutralization titers against SARS-CoV-2 Delta were impaired in both age groups compared with SARS-CoV-2 WT, thereby emphasizing the need for an additional booster to overcome rising variants of SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: Age-dependent immune responses after BNT162b2; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; SARS-CoV-2 vaccination; T cell immunity; neutralizing antibodies; variants of concern (VOCs); virus neutralization.
Copyright © 2022 Jäger, Sonnleitner, Dichtl, Lafon, Diem, Walder, Lass-Flörl, Wilflingseder and Posch.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors SS and GW were employed by Dr. Gernot Walder GmbH, Ausservillgraten, Austria. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

