Penpulimab, an Fc-Engineered IgG1 Anti-PD-1 Antibody, With Improved Efficacy and Low Incidence of Immune-Related Adverse Events
- PMID: 35833116
- PMCID: PMC9272907
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.924542
Penpulimab, an Fc-Engineered IgG1 Anti-PD-1 Antibody, With Improved Efficacy and Low Incidence of Immune-Related Adverse Events
Abstract
Background: IgG4 anbibodies are deficient in stability and may contribute to tumor-associated escape from immune surveillance. We developed an IgG1 backbone anti-programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) antibody, penpulimab, which is designed to remove crystallizable fragment (Fc) gamma receptor (FcγR) binding that mediates antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP) and proinflammatory cytokine release.
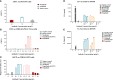
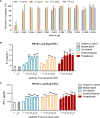
Methods: Aggregation of different anti-PD-1 antibodies was tested by size exclusion chromatography, and melting temperature midpoint (Tm) and aggregation temperature onset (Tagg) were also determined. The affinity constants of penpulimab for PD-1 and human FcγRs were measured by surface plasmon resonance and biolayer interferometry. ADCC and ADCP were determined in cellular assays and antibody-dependent cytokine release (ADCR) from human macrophages was detected by ELISA. Binding kinetics of penpulimab to human PD-1 was determined by Biacore, and epitope/paratope mapping of PD-1/penpulimab was investigated using x-ray crystallography. Additionally, patients from six ongoing trials were included for analysis of immune-related adverse events (irAEs).
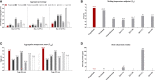
Results: Penpulimab demonstrated better stability and a lower level of host-cell protein residue compared with IgG4 backbone anti-PD-1 antibodies. As expected, penpulimab exhibited no apparent binding to FcγRIa, FcγRIIa_H131, FcγRIIIa_V158 and FcγRIIIa_F158, elicited no apparent ADCC and ADCP activities, and induced no remarkable IL-6 and IL-8 release by activated macrophages in vitro. Penpulimab was shown in the co-crystal study to bind to human PD-1 N-glycosylation site at N58 and had a slower off-rate from PD-1 versus nivolumab or pembrolizumab. Four hundred sixty-five patients were analyzed for irAEs. Fifteen (3.2%) patients had grade 3 or above irAEs. No death from irAEs was reported.
Conclusions: IgG1 backbone anti-PD1 antibody penpulimab has a good stability and reduced host cell protein residue, as well as potent binding to the antigen. Fc engineering has eliminated Fc-mediated effector functions of penpulimab including ADCC, ADCP and reduced ADCR, which may contribute to its more favorable safety profile.
Clinical trial registration: www.ClinicalTrials.gov, identifier: AK105-101: NCT03352531, AK105-201: NCT03722147, AK105-301: NCT03866980, AK105-202:NCT03866967, AK105-203: NCT04172571, AK105-204: NCT04172506.
Keywords: Fc engineering; IgG1 anti-PD-1 antibody; binding kinetics; immune-related adverse events; penpulimab.
Copyright © 2022 Huang, Pang, Zhong, Qu, Chen, Ma, He, Xia, Wang, Xia and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are employees of Akeso Biopharma Co., Ltd., who participated in the discovery, production and commercialization of penpulimab.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An Fc engineering approach that modulates antibody-dependent cytokine release without altering cell-killing functions.MAbs. 2015;7(3):494-504. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2015.1022692. MAbs. 2015. PMID: 25933349 Free PMC article.
-
Phase 1b/2 study of penpulimab (AK105), an antiprogrammed cell death-1 immunoglobulin G1 antibody, in advanced or metastatic solid tumors (AK105-204).Cancer. 2024 Jun 15;130(12):2180-2190. doi: 10.1002/cncr.35259. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38412283 Clinical Trial.
-
Full-length recombinant antibodies from Escherichia coli: production, characterization, effector function (Fc) engineering, and clinical evaluation.MAbs. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2111748. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2022.2111748. MAbs. 2022. PMID: 36018829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Penpulimab for Relapsed or Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Multicenter, Single-Arm, Pivotal Phase I/II Trial (AK105-201).Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 7;12:925236. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.925236. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35875118 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Fcγ receptors in HER2-targeted breast cancer therapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Jan;10(1):e003171. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003171. J Immunother Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34992090 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Penpulimab combined with anlotinib in patients with R/M HNSCC after failure of platinum-based chemotherapy: a single-arm, multicenter, phase Ⅱ study.ESMO Open. 2023 Dec;8(6):102194. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2023.102194. Epub 2023 Dec 14. ESMO Open. 2023. PMID: 38100934 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Fc-Fc interactions and immune inhibitory effects of IgG4: implications for anti-PD-1 immunotherapies.J Immunother Cancer. 2024 Jun 25;12(6):e009034. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-009034. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38925680 Free PMC article.
-
B7 family protein glycosylation: Promising novel targets in tumor treatment.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 6;13:1088560. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1088560. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36561746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of a fragment crystallizable-engineered tetravalent bispecific antibody targeting programmed cell death-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor with cooperative biological effects.iScience. 2024 Dec 31;28(3):111722. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111722. eCollection 2025 Mar 21. iScience. 2024. PMID: 40034861 Free PMC article.
-
Locoregional radiotherapy improves survival outcomes in de novo metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with chemoimmunotherapy.ESMO Open. 2023 Oct;8(5):101629. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2023.101629. Epub 2023 Sep 1. ESMO Open. 2023. PMID: 37660406 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

