N-Glycosylation and Inflammation; the Not-So-Sweet Relation
- PMID: 35833138
- PMCID: PMC9272703
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.893365
N-Glycosylation and Inflammation; the Not-So-Sweet Relation
Abstract
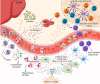
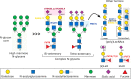
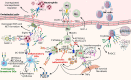
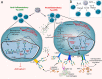
Chronic inflammation is the main feature of many long-term inflammatory diseases such as autoimmune diseases, metabolic disorders, and cancer. There is a growing number of studies in which alterations of N-glycosylation have been observed in many pathophysiological conditions, yet studies of the underlying mechanisms that precede N-glycome changes are still sparse. Proinflammatory cytokines have been shown to alter the substrate synthesis pathways as well as the expression of glycosyltransferases required for the biosynthesis of N-glycans. The resulting N-glycosylation changes can further contribute to disease pathogenesis through modulation of various aspects of immune cell processes, including those relevant to pathogen recognition and fine-tuning the inflammatory response. This review summarizes our current knowledge of inflammation-induced N-glycosylation changes, with a particular focus on specific subsets of immune cells of innate and adaptive immunity and how these changes affect their effector functions, cell interactions, and signal transduction.
Keywords: N-glycans; N-glycosylation; cytokines; immunity; immunoglobulins; inflammation; leukocytes.
Copyright © 2022 Radovani and Gudelj.
Conflict of interest statement
Author IG was employed by Genos Glycoscience. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
How glycosylation affects glycosylation: the role of N-glycans in glycosyltransferase activity.Glycobiology. 2020 Dec 9;30(12):941-969. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwaa041. Glycobiology. 2020. PMID: 32363402 Review.
-
Role of Cytokine-Induced Glycosylation Changes in Regulating Cell Interactions and Cell Signaling in Inflammatory Diseases and Cancer.Cells. 2016 Nov 29;5(4):43. doi: 10.3390/cells5040043. Cells. 2016. PMID: 27916834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infection and the Glycome─New Insights into Host Response.ACS Infect Dis. 2024 Aug 9;10(8):2540-2550. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.4c00315. Epub 2024 Jul 11. ACS Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38990078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycosylation changes in inflammatory diseases.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2020;119:111-156. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2019.08.008. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2020. PMID: 31997767 Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation of the vascular endothelial glycome by angiogenic and inflammatory signalling.Angiogenesis. 2010 Mar;13(1):25-42. doi: 10.1007/s10456-010-9162-4. Epub 2010 Feb 17. Angiogenesis. 2010. PMID: 20162350
Cited by
-
Hyperglycosylation as an Indicator of Aging in the Bone Metabolome of Oryzias latipes.Metabolites. 2024 Sep 27;14(10):525. doi: 10.3390/metabo14100525. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 39452906 Free PMC article.
-
The association between plasma IgG N-glycosylation and neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a case-control study.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Mar 20;18:1335688. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1335688. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38572072 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosylation Targeting: A Paradigm Shift in Cancer Immunotherapy.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Apr 22;20(7):2607-2621. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.93806. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38725856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting protein glycosylation to regulate inflammation in the respiratory tract: novel diagnostic and therapeutic candidates for chronic respiratory diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 May 15;14:1168023. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1168023. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37256139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-8 Downregulation Mediates the Beneficial Effects of Infection-Induced Fever on Breast Cancer Prognosis.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Jan 8;18:405-419. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S496099. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 39802515 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

