Safety of fexofenadine and other second-generation oral antihistamines before and after the removal of the prescription requirement in Italy and other European countries: A real-world evidence study and systematic review
- PMID: 35833202
- PMCID: PMC9260294
- DOI: 10.1016/j.waojou.2022.100658
Safety of fexofenadine and other second-generation oral antihistamines before and after the removal of the prescription requirement in Italy and other European countries: A real-world evidence study and systematic review
Abstract
Background: The change from prescription to over-the-counter (OTC) status of oral antihistamines may raise concerns about drug safety due to the possibility of misuse/abuse. In most European countries, oral antihistamines are available without prescription, whereas in Italy, only <10-tablet packs are available OTC.
Objectives: To evaluate the safety profile of fexofenadine after OTC switch in Italy in a real-world setting, and to compare its safety profile to that of other European countries where larger pack sizes are available. To compare the safety of fexofenadine, cetirizine, and loratadine in Italy. To examine safety/efficacy across Europe with a systematic review.
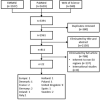
Methods: This case-by-case analysis used the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) adverse event reporting system (FAERS) to extract data of the adverse events (AEs) related to fexofenadine, loratadine and cetirizine in Italy January 2010-June 2020. The year 2016 was taken as the index date (removal of prescription requirement) for evaluation of the reporting trend of AEs of fexofenadine in Italy and make a comparison pre/post-OTC switch. A comparison of AEs with other European countries where fexofenadine is sold OTC in large packs >20 tablets (Belgium, Portugal, Switzerland, Finland, Hungary) was made. The rate at which an AE related to oral antihistamines occurred was estimated by calculation of the reporting rate (number of cases/[defined daily dose/1000 inhabitants per day]) on the basis of IQVIA sales data using the Italian Institute of Statistics database. A systematic review of the literature was also performed.
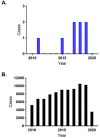
Results: There were 3760 reports of AEs with a suspected association with fexofenadine; of these, eight were reported from Italy. There was a slightly increasing trend per year, in line with a general reporting trend of other drugs. In European countries where fexofenadine is available, the impact of OTC switch on AE reporting activity was negligible: from 2016, the reporting rate increased slightly and then normalized at 3.01, an incidence value similar to that recorded before the OTC switch (3.7 in 2015). Of 22 studies included in the systematic review, 18 (82%) positively evaluated the OTC use of oral antihistamines, confirming an acceptable safety/tolerability profile.
Conclusion: There was no difference in number of AEs reported for fexofenadine pre/post-OTC switch, indicating a similar safety profile. Spontaneous reporting systems are a valuable source of real-world data and support the OTC provision of oral antihistamines in Europe and fexofenadine in Italy, in addition to supporting the use of larger pack sizes in Italy.
Keywords: Fexofenadine; Food and drug administration adverse event reporting system (FAERS); Over-the-counter (OTC); Pharmacovigilance; Second-generation oral antihistamines.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pro-arrhythmic potential of oral antihistamines (H1): combining adverse event reports with drug utilization data across Europe.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 18;10(3):e0119551. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119551. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25785934 Free PMC article.
-
Data mining in FAERS: association of newer-generation H1-antihistamines with nervous system disorders.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2024 Dec 18;25(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s40360-024-00822-x. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39696617 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of product switching after a state Medicaid program began covering loratadine OTC 1 year after market availability.J Manag Care Pharm. 2006 Mar;12(2):108-20. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2006.12.2.108. J Manag Care Pharm. 2006. PMID: 16515369 Free PMC article.
-
Antihistamine effects and safety of fexofenadine: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019 Nov 29;20(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s40360-019-0363-1. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31783781 Free PMC article.
-
Focus on Over-the-Counter Drugs' Misuse: A Systematic Review on Antihistamines, Cough Medicines, and Decongestants.Front Psychiatry. 2021 May 7;12:657397. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.657397. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34025478 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Update meta-analysis on the efficacy and safety issues of fexofenadine.World Allergy Organ J. 2023 Jul 11;16(7):100795. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2023.100795. eCollection 2023 Jul. World Allergy Organ J. 2023. PMID: 37546236 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Fexofenadine: A Systematic Review.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Dec 20;16(12):1619. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16121619. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39771597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-risks drug adverse events associated with Cetirizine and Loratadine for the treatment of allergic diseases: A retrospective pharmacovigilance study based on the FDA adverse event reporting system database.Clin Transl Allergy. 2024 Sep;14(9):e12392. doi: 10.1002/clt2.12392. Clin Transl Allergy. 2024. PMID: 39257032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zaprutko T., Kopciuch D., Ratajczak P., et al. The prescription to over-the-counter switches and double registration of medicines - the perspective of pharmacists from the Greater Poland. Clin Exp Allergy. 2019;76:907–912.
-
- Association CHP . 2022. Rx-to-OTC Switch.https://www.chpa.org/our-issues/otc-medicines/rx-otc-switch Available from:
-
- Stippler A., Eckstein N., Kroth E. To switch or not to switch—first Germany-wide study from the perspective of pharmacists in the European environment. J Public Health. 2021;29(1):9–17.
-
- Devillier P., Roche N., Faisy C. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of desloratadine, fexofenadine and levocetirizine: a comparative review. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2008;47(4):217–230. - PubMed
-
- Bilkhu P.S., Wolffsohn J.S., Naroo S.A. A review of non-pharmacological and pharmacological management of seasonal and perennial allergic conjunctivitis. Contact Lens Anterior Eye: J Br Contact Lens Assoc. 2012;35(1):9–16. - PubMed

