Oral characteristics in adult individuals with periodontal Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- PMID: 35833531
- PMCID: PMC9796896
- DOI: 10.1111/jcpe.13698
Oral characteristics in adult individuals with periodontal Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Abstract
Aim: Periodontal Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (pEDS) is a monogenic type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome characterized by periodontal destruction at a young age. The present study aimed to document the oral phenotype of pEDS based on prospective clinical investigations.
Materials and methods: Thirty-five adult individuals from 13 families with a clinically and genetically confirmed diagnosis of pEDS underwent a systematic oral assessment.
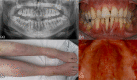
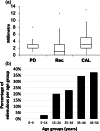
Results: Periodontitis stage 3 or 4 or edentulism due to periodontal destruction were diagnosed in 94% of the individuals. First permanent tooth loss was reported at the age of 21.5 years (median; range 13-43 years). Deep periodontal pockets were infrequent, with 94% measuring <4 mm. However, there was increased clinical attachment loss (CAL) averaging 8 mm (range 4-13 mm), and the probability of being edentate between the age of 35 and 44 years was 28-47% compared with less than 0.25% of the general population. Radiographic anomalous findings were only found in a portion of subjects and consisted of fused roots of maxillary second molars (81%), root hypoplasia (57%), taurodontism (26%) and tooth rotation of premolars (67%). As such, radiographic findings are not considered common characteristics of pEDS.
Conclusions: Characteristic oral traits of pEDS in adults are severe CAL with shallow probing depths and marked gingival recession. This is complemented by a lack of attached gingiva. These indications need to be paralleled by genetic analyses to diagnose pEDS unambiguously.
Keywords: C1R; C1S; Ehlers-Danlos syndrome; attached gingiva; periodontitis.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Periodontology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bally, I. , Dalonneau, F. , Chouquet, A. , Grobner, R. , Amberger, A. , Kapferer‐Seebacher, I. , Stoiber, H. , Zschocke, J. , Thielens, N. M. , Rossi, V. , & Gaboriaud, C. (2019). Two different missense C1S mutations, associated to periodontal Ehlers‐Danlos syndrome, lead to identical molecular outcomes. Frontiers in Immunology, 10, 2962. 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02962 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

