Investigating the role of RNA structures in transcriptional pausing using in vitro assays and in silico analyses
- PMID: 35833713
- PMCID: PMC9291695
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2022.2096794
Investigating the role of RNA structures in transcriptional pausing using in vitro assays and in silico analyses
Abstract
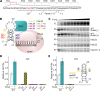
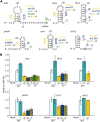
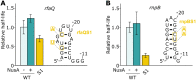
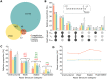
Transcriptional pausing occurs across the bacterial genome but the importance of this mechanism is still poorly understood. Only few pauses were observed during the previous decades, leaving an important gap in understanding transcription mechanisms. Using the well-known Escherichia coli hisL and trpL pause sites as models, we describe here the relation of pause sites with upstream RNA structures suspected to stabilize pausing. We find that the transcription factor NusA influences the pause half-life at leuL, pheL and thrL pause sites. Using a mutagenesis approach, we observe that transcriptional pausing is affected in all tested pause sites, suggesting that the upstream RNA sequence is important for transcriptional pausing. Compensatory mutations assessing the presence of RNA hairpins did not yield clear conclusions, indicating that complex RNA structures or transcriptional features may be playing a role in pausing. Moreover, using a bioinformatic approach, we explored the relation between a DNA consensus sequence important for pausing and putative hairpins among thousands of pause sites in E. coli. We identified 2125 sites presenting hairpin-dependent transcriptional pausing without consensus sequence, suggesting that this mechanism is widespread across E. coli. This study paves the way to understand the role of RNA structures in transcriptional pausing.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; RNA polymerase; Transcription; hisL; pause.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
