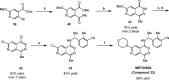
Design and Discovery of MRTX0902, a Potent, Selective, Brain-Penetrant, and Orally Bioavailable Inhibitor of the SOS1:KRAS Protein-Protein Interaction
- PMID: 35833726
- PMCID: PMC9340770
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00741
Design and Discovery of MRTX0902, a Potent, Selective, Brain-Penetrant, and Orally Bioavailable Inhibitor of the SOS1:KRAS Protein-Protein Interaction
Abstract
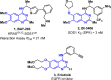
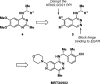
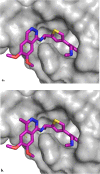
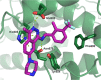
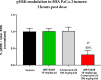
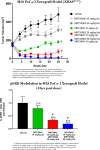
SOS1 is one of the major guanine nucleotide exchange factors that regulates the ability of KRAS to cycle through its "on" and "off" states. Disrupting the SOS1:KRASG12C protein-protein interaction (PPI) can increase the proportion of GDP-loaded KRASG12C, providing a strong mechanistic rationale for combining inhibitors of the SOS1:KRAS complex with inhibitors like MRTX849 that target GDP-loaded KRASG12C. In this report, we detail the design and discovery of MRTX0902─a potent, selective, brain-penetrant, and orally bioavailable SOS1 binder that disrupts the SOS1:KRASG12C PPI. Oral administration of MRTX0902 in combination with MRTX849 results in a significant increase in antitumor activity relative to that of either single agent, including tumor regressions in a subset of animals in the MIA PaCa-2 tumor mouse xenograft model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): All authors of this manuscript are employees of Mirati Therapeutics.
Figures
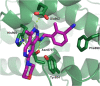
References
-
- Bos J. L. Ras Oncogenes in Human Cancer: A Review. Cancer Res. 1989, 49 (17), 4682–4689. - PubMed
-
- Fell J. B.; Fischer J. P.; Baer B. R.; Blake J. F.; Bouhana K.; Briere D. M.; Brown K. D.; Burgess L. E.; Burns A. C.; Burkard M. R.; Chiang H.; Chicarelli M. J.; Cook A. W.; Gaudino J. J.; Hallin J.; Hanson L.; Hartley D. P.; Hicken E. J.; Hingorani G. P.; Hinklin R. J.; Mejia M. J.; Olson P.; Otten J. N.; Rhodes S. P.; Rodriguez M. E.; Savechenkov P.; Smith D. J.; Sudhakar N.; Sullivan F. X.; Tang T. P.; Vigers G. P.; Wollenberg L.; Christensen J. G.; Marx M. A. Identification of the Clinical Development Candidate MRTX849, a Covalent KRAS G12C Inhibitor for the Treatment of Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63 (13), 6679–6693. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b02052. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ou S.-H. I.; Jänne P. A.; Leal T. A.; Rybkin I. I.; Sabari J. K.; Barve M. A.; Bazhenova L. A.; Johnson M. L.; Velastegui K. L.; Cilliers C.; Christensen J. G.; Yan X.; Chao R. C.; Papadopoulos K. P. First-in-Human Phase I/IB Dose-Finding Study of Adagrasib (MRTX849) in Patients With Advanced KRASG12C Solid Tumors (KRYSTAL-1). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 10.1200/JCO.21.02752. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bekaii-Saab T. S.; Spira A. I.; Yaeger R.; Buchschacher G. L.; McRee A. J.; Sabari J. K.; Johnson M. L.; Barve M. A.; Hafez N.; Velastegui K.; Christensen J. G.; Kheoh T.; Der-Torossian H.; Rybkin I. I. KRYSTAL-1: Updated Activity and Safety of Adagrasib (MRTX849) in Patients (Pts) with Unresectable or Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer (PDAC) and Other Gastrointestinal (GI) Tumors Harboring a KRAS G12C Mutation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 519.10.1200/JCO.2022.40.4_suppl.519. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

