Gastrointestinal Bleeding in COVID-19 Patients: A Rapid Review
- PMID: 35833732
- PMCID: PMC9328937
- DOI: 10.1097/SGA.0000000000000676
Gastrointestinal Bleeding in COVID-19 Patients: A Rapid Review
Abstract
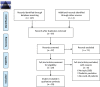
The incidence of COVID-19 gastrointestinal manifestations has been reported to range from 3% to 61%. There are limited data on the incidence rates and risk factors associated with gastrointestinal bleeding (GIB) in patients with COVID-19. A rapid review has been designed to investigate whether there is a relationship between COVID-19 and GIB in adult patients. PubMed, CINAHL, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, and Scopus databases have been analyzed. A total of 129 studies were found; 29 full texts were analyzed, and of these, 20 were found to be relevant to the topic. The key findings of the included studies present an overall GIB rate in COVID-19 patients ranging from 1.1% to 13%. The bleeding involves mucosal damage of the duodenum, stomach, colon, and rectum. The management of gastrointestinal bleeding could be conservative. The use of fecal diversion systems for the management of diarrhea in COVID-19 patients should be minimized and closely evaluated for the risk of rectal mucosal damages and erosions. It is recommended to provide an accurate nutritional assessment; an early setting up of enteral nutrition, if not contraindicated, can help protect the gut mucosa of patients and restore normal intestinal flora. Larger cohort studies are needed to increase the information about this topic.
Copyright © 2022 Society of Gastroenterology Nurses and Associates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bambi S., Mati E., De Felippis C., Lucchini A. (2017). Enteral nutrition during noninvasive ventilation: We should go deeper in the investigation. Respiratory Care, 62(8), 1118–1119. doi:10.4187/respcare.05509 - PubMed
-
- Bruni A., Garofalo E., Grande L., Auletta G., Cubello D., Greco M., Longhini F. (2020). Nursing issues in enteral nutrition during prone position in critically ill patients: A systematic review of the literature. Intensive and Critical Care Nursing, 60, 102899. doi:10.1016/j.iccn.2020.102899 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

