Autoimmunity and SARS-CoV-2 infection: Unraveling the link in neurological disorders
- PMID: 35833748
- PMCID: PMC9350097
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.202149475
Autoimmunity and SARS-CoV-2 infection: Unraveling the link in neurological disorders
Abstract
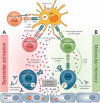
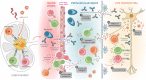
According to the World Health Organization, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has already infected more than 400 million people and caused over 5 million deaths globally. The infection is associated with a wide spectrum of clinical manifestations, ranging from no signs of illness to severe pathological complications that go beyond the typical respiratory symptoms. On this note, new-onset neurological and neuropsychiatric syndromes have been increasingly reported in a large fraction of COVID-19 patients, thus potentially representing a significant public health threat. Although the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms remain elusive, a growing body of evidence suggests that SARS-CoV-2 infection may trigger an autoimmune response, which could potentially contribute to the establishment and/or exacerbation of neurological disorders in COVID-19 patients. Shedding light on this aspect is urgently needed for the development of effective therapeutic intervention. This review highlights the current knowledge of the immune responses occurring in Neuro-COVID patients and discusses potential immune-mediated mechanisms by which SARS-CoV-2 infection may trigger neurological complications.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; autoimmunity, COVID-19, neuro-COVID, neuroimmunology.
© 2022 The Authors. European Journal of Immunology published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no commercial or financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Spudich, S. and Nath, A. , Nervous system consequences of COVID‐19. Science 2022. 375: 267–269. - PubMed
-
- Chou, S. H. , Beghi, E. , Helbok, R. , Moro, E. , Sampson, J. , Altamirano, V. , Mainali, S. et al., Global incidence of neurological manifestations among patients hospitalized with COVID‐19‐A report for the GCS‐NeuroCOVID consortium and the ENERGY Consortium. JAMA Netw. Open 2021. 4: e2112131. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ross Russell, A. L. , Hardwick, M. , Jeyanantham, A. , White, L. M. , Deb, S. , Burnside, G. , Joy, H. M. et al., Spectrum, risk factors and outcomes of neurological and psychiatric complications of COVID‐19: a UK‐wide cross‐sectional surveillance study. Brain Commun. 2021. 3: fcab168. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

