Effect of Paclitaxel Stereochemistry on X-ray-Triggered Release of Paclitaxel from CaWO4/Paclitaxel-Coloaded PEG-PLA Nanoparticles
- PMID: 35834797
- PMCID: PMC11975462
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00148
Effect of Paclitaxel Stereochemistry on X-ray-Triggered Release of Paclitaxel from CaWO4/Paclitaxel-Coloaded PEG-PLA Nanoparticles
Erratum in
-
Correction to "Effect of Paclitaxel Stereochemistry on X-ray-Triggered Release of Paclitaxel from CaWO4/Paclitaxel-Coloaded PEG-PLA Nanoparticles".Mol Pharm. 2023 Aug 7;20(8):4331-4334. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.3c00510. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Mol Pharm. 2023. PMID: 37477492 No abstract available.
Abstract
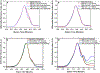
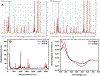
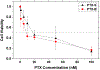
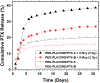
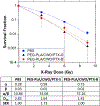
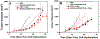
For many locally advanced tumors, the chemotherapy-radiotherapy (CT-RT) combination ("chemoradiation") is currently the standard of care. Intratumoral (IT) CT-based chemoradiation has the potential to overcome the limitations of conventional systemic CT-RT (side effects). For maximizing the benefits of IT CT-RT, our laboratory has previously developed a radiation-controlled drug release formulation, in which anticancer drug paclitaxel (PTX) and radioluminescent CaWO4 (CWO) nanoparticles (NPs) are co-encapsulated with poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactic acid) (PEG-PLA) block copolymers ("PEG-PLA/CWO/PTX NPs"). These PEG-PLA/CWO/PTX NPs enable radiation-controlled release of PTX and are capable of producing sustained therapeutic effects lasting for at least one month following a single IT injection. The present article focuses on discussing our recent finding about the effect of the stereochemical structure of PTX on the efficacy of this PEG-PLA/CWO/PTX NP formulation. Stereochemical differences in two different PTX compounds ("PTX-S" from Samyang Biopharmaceuticals and "PTX-B" from Biotang) were characterized by 2D heteronuclear/homonuclear NMR, Raman spectroscopy, and circular dichroism measurements. The difference in PTX stereochemistry was found to significantly influence their water solubility (WS); PTX-S (WS ≈ 4.69 μg/mL) is about 19 times more water soluble than PTX-B (WS ≈ 0.25 μg/mL). The two PTX compounds showed similar cancer cell-killing performances in vitro when used as free drugs. However, the subtle stereochemical difference significantly influenced their X-ray-triggered release kinetics from the PEG-PLA/CWO/PTX NPs; the more water-soluble PTX-S was released faster than the less water-soluble PTX-B. This difference was manifested in the IT pharmacokinetics and eventually in the survival percentages of test animals (mice) treated with PEG-PLA/CWO/PTX NPs + X-rays in an in vivo human tumor xenograft study; at short times (<1 month), concurrent PEG-PLA/CWO/PTX-S NPs produced a greater tumor-suppression effect, whereas PEG-PLA/CWO/PTX-B NPs had a longer-lasting radio-sensitizing effect. This study demonstrates the importance of the stereochemistry of a drug in a therapy based on a controlled release formulation.
Keywords: paclitaxel; poly(ethylene glycol)−poly(D,L-lactic acid); radiation-controlled drug release; radioluminescent CaWO4 nanoparticle; stereochemistry.
Figures



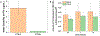

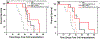
Similar articles
-
Radioluminescent nanoparticles for radiation-controlled release of drugs.J Control Release. 2019 Jun 10;303:237-252. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.04.033. Epub 2019 Apr 23. J Control Release. 2019. PMID: 31026550
-
Development and evaluation of novel tumor-targeting paclitaxel-loaded nano-carriers for ovarian cancer treatment: in vitro and in vivo.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Feb 26;37(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0700-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29478415 Free PMC article.
-
Oligo(lactic acid)n-Paclitaxel Prodrugs for Poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(lactic acid) Micelles: Loading, Release, and Backbiting Conversion for Anticancer Activity.J Am Chem Soc. 2016 Jul 20;138(28):8674-7. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b03995. Epub 2016 Jul 11. J Am Chem Soc. 2016. PMID: 27374999 Free PMC article.
-
PEG-PLA-Coated and Uncoated Radio-Luminescent CaWO4 Micro- and Nanoparticles for Concomitant Radiation and UV-A/Radio-Enhancement Cancer Treatments.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018 Apr 9;4(4):1445-1462. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b00119. Epub 2018 Mar 2. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018. PMID: 33418674
-
PEG-b-PLA micelles and PLGA-b-PEG-b-PLGA sol-gels for drug delivery.J Control Release. 2016 Oct 28;240:191-201. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.12.015. Epub 2015 Dec 15. J Control Release. 2016. PMID: 26699425 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Martin V, Overview of paclitaxel (TAXOL), Semin Oncol Nurs, 9 (1993) 2–5. - PubMed
-
- H.a.B. MAa.B. Sa.P. FHa.A. FJ, Nanopaclitaxel therapy: an evidence based review on the battle for next-generation formulation challenges, Nanomedicine, 14 (2019) 1323–1341. - PubMed
-
- M. Amanda Starling-Windhof and Asur Srinivasan and Tina Tomeo and Anne Marie Clark and Peter, Chapter 10 - Trends in the intellectual property (IP) landscape of drug delivery systems: 30 years of growth and evolution, (2020) 201–230.
-
- Song JI, Dumais MR, From yew to us: the curious development of taxol, Jama, 266 (1991) 1281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

