Single-Domain Antibody Theranostics on the Horizon
- PMID: 35835579
- PMCID: PMC9536702
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.122.263907
Single-Domain Antibody Theranostics on the Horizon
Abstract
Single-domain antibody (sdAb) is among the most promising vectors for developing molecular imaging tracers. Several sdAb tracers targeting human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 or programmed death ligand 1 have entered clinical practice. However, radiolabeled single-valent sdAbs generally have high kidney retention, limiting their therapeutic applications. Therefore, engineering strategies such as PEGylation or incorporation of renal cleavable linkers can be adapted to improve pharmacokinetics and reduce kidney retention. In this Focus on Molecular Imaging review, we try to summarize the latest developments in sdAb-derived agents and propose potential strategies that can be used to improve the theranostic value of radiolabeled sdAbs.
Keywords: cancer; immuno-PET; nanobody; radiopharmaceuticals; theranostics.
© 2022 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures
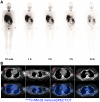
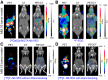
References
-
- Mankoff DA. A definition of molecular imaging. J Nucl Med. 2007;48(6):18N, 21N. - PubMed
-
- Xavier C, Vaneycken I, D’Huyvetter M, et al. . Synthesis, preclinical validation, dosimetry, and toxicity of 68Ga-NOTA-anti-HER2 Nanobodies for iPET imaging of HER2 receptor expression in cancer. J Nucl Med. 2013;54:776–784. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
