Non-monotonous dose response function of the termination of spiral wave chaos
- PMID: 35835979
- PMCID: PMC9283470
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-16068-8
Non-monotonous dose response function of the termination of spiral wave chaos
Abstract
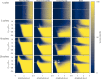
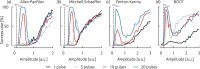
The conventional termination technique of life threatening cardiac arrhythmia like ventricular fibrillation is the application of a high-energy electrical defibrillation shock, coming along with severe side-effects. In order to improve the current treatment reducing these side-effects, the application of pulse sequences of lower energy instead of a single high-energy pulse are promising candidates. In this study, we show that in numerical simulations the dose-response function of pulse sequences applied to two-dimensional spiral wave chaos is not necessarily monotonously increasing, but exhibits a non-trivial frequency dependence. This insight into crucial phenomena appearing during termination attempts provides a deeper understanding of the governing termination mechanisms in general, and therefore may open up the path towards an efficient termination of cardiac arrhythmia in the future.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

