A comprehensive prognostic and immune analysis of enhancer RNA identifies IGFBP7-AS1 as a novel prognostic biomarker in Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma
- PMID: 35836132
- PMCID: PMC9284715
- DOI: 10.1186/s12575-022-00172-0
A comprehensive prognostic and immune analysis of enhancer RNA identifies IGFBP7-AS1 as a novel prognostic biomarker in Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNA) have been implicated in a hand of studies that supported an involvement and co-operation in Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma (UCEC). Enhancer RNAs (eRNA), a functional subtype of lncRNA, have a key role throughout the genome to guide protein production, thus potentially associated with diseases.
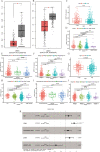
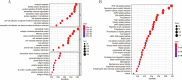
Methods: In this study, we mainly applied the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset to systematically discover crucial eRNAs involving UCEC. For the key eRNAs in UCEC, we employed RT-qPCR to compare eRNA expression levels in tumor tissues and paired normal adjacent tissues from UCEC patients for validation. Furthermore, the relationships between the key eRNAs and immune activities were measured from several aspects, including the analysis for tumor microenvironment, immune infiltration cells, immune check point genes, tumor mutation burden, and microsatellite instability, as well as m6A related genes. Finally, the key eRNAs were verified by a comprehensive pan-cancer analysis.
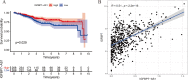
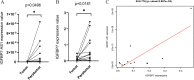
Results: IGFBP7 Antisense RNA 1 (IGFBP7-AS1) was identified as the key eRNA for its expression patterns of low levels in tumor tissues and favorable prognostic value in UCEC correlated with its target gene IGFBP7. In RT-qPCR analysis, IGFBP7-AS1 and IGFBP7 had down-regulated expression in tumor tissues, which was consistent with previous analysis. Moreover, IGFBP7-AS1 was found closely related with immune response in relevant immune analyses. Besides, IGFBP7-AS1 and its target gene IGFBP7 correlated with a multi-omics pan-cancer analysis.
Conclusions: Finally, we suggested that IGFBP7-AS1 played a key role in impacting on clinical outcomes of UCEC patients for its possible influence on immune activity.
Keywords: Enhancer RNA; IGFBP7; IGFBP7-AS1; Tumor immunity; UCEC.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

