Arecoline promotes proliferation and migration of human HepG2 cells through activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
- PMID: 35836300
- PMCID: PMC9281068
- DOI: 10.1186/s41065-022-00241-0
Arecoline promotes proliferation and migration of human HepG2 cells through activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
Abstract
Background: Arecoline is a well-known risk factor for oral submucosal fibrosis and cancer. However, the mechanistic correlation between arecoline and hepatocellular cancer remains elusive. Here, we investigated the effect of arecoline on the proliferation and migration of human HepG2 hepatoma cells and its potential oncogenic mechanisms.
Methods: Bioinformatic technologies were used to identify the deferentially expressed miRNAs (DE-miRNAs) and hub target genes of arecoline-induced cancers. These DE-miRNAs, hub genes and pathway were proved in arecoline-treated HepG2 cells.
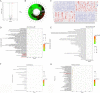
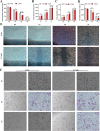
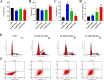
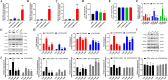
Results: A total of 86 DE-miRNAs and 460 target genes were identified. These target genes are associated with DNA-templated regulation of transcription and other biological processes. Significant molecular functions were protein binding, calcium ion binding, and enrichment in the nucleus and cytoplasm. These genes are involved in the PI3K-AKT pathway. CDK1, CCND1, RAF1, CDKN1B and BTRC were defined as the top 5 hub target genes, and patients with high expression of CDK1 showed poor prognosis. Compared with control group, 2.5 µM arecoline treatment increased the proliferation and migration ability of the HepG2 cells. Treatment with 2.5 µM arecoline increased the levels of miR-21-3p, miR-21-5p and miR-1267, upregulated the expression of PI3K-AKT pathway factors, CDK1, CCND1 but decreased RAF1 expression.
Conclusion: A low concentration arecoline can induce the proliferation and migration of HepG2 cells, with the potential mechanism of action linked to high levels of exosomal miR-21 and miR-1267, activation of the PI3K-AKT pathway, upregulation of CDK1 and CCND1, and downregulation of RAF1.
Keywords: Arecoline; CDK1; Cell migration; Cell proliferation; Hepatocellular cancer; PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Kaempferol inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of liver cancer HepG2 cells by down-regulation of microRNA-21.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2018 Mar-Dec;32:2058738418814341. doi: 10.1177/2058738418814341. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2018. Retraction in: Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2021 Jan-Dec;35:20587384211040394. doi: 10.1177/20587384211040394. PMID: 30477356 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
MicroRNA-99b suppresses human cervical cancer cell activity by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):9577-9591. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27645. Epub 2018 Nov 27. J Cell Physiol. 2019. Retraction in: J Cell Physiol. 2022 Mar;237(3):2008. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30520. PMID: 30480801 Retracted.
-
MiR-155-5p exerts tumor-suppressing functions in Wilms tumor by targeting IGF2 via the PI3K signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 May;125:109880. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109880. Epub 2020 Jan 28. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32004974
-
Role of regulatory miRNAs of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cell Physiol. 2020 May;235(5):4146-4152. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29333. Epub 2019 Oct 29. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31663122 Review.
-
Detailed role of microRNA-mediated regulation of PI3K/AKT axis in human tumors.Cell Biochem Funct. 2024 Jan;42(1):e3904. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3904. Epub 2023 Dec 16. Cell Biochem Funct. 2024. PMID: 38102946 Review.
Cited by
-
The Controversial Roles of Areca Nut: Medicine or Toxin?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 19;24(10):8996. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108996. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive insights into areca nut: active components and omics technologies for bioactivity evaluation and quality control.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 30;15:1407212. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1407212. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38873426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic Review of Roles of Arecoline and Arecoline N-Oxide in Oral Cancer and Strategies to Block Carcinogenesis.Cells. 2023 Apr 21;12(8):1208. doi: 10.3390/cells12081208. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37190117 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agents in chronic liver diseases: Molecular mechanisms and therapy.World J Hepatol. 2023 Feb 27;15(2):180-200. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i2.180. World J Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36926234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening microRNAs as potential prognostic biomarkers for lung adenocarcinoma.Ann Med. 2023;55(2):2241013. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2241013. Epub 2023 Nov 6. Ann Med. 2023. PMID: 37930873 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

