Bcl-2 19-kDa Interacting Protein 3 (BNIP3)-Mediated Mitophagy Attenuates Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Human Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Injury
- PMID: 35836356
- PMCID: PMC9295414
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.936760
Bcl-2 19-kDa Interacting Protein 3 (BNIP3)-Mediated Mitophagy Attenuates Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Human Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Injury
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Bcl-2 19-kDa Interacting Protein 3 (BNIP3)-Mediated Mitophagy Attenuates Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Human Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Injury.Med Sci Monit. 2023 Jan 31;29:e939597. doi: 10.12659/MSM.939597. Med Sci Monit. 2023. PMID: 36718665 Free PMC article.
Abstract
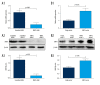
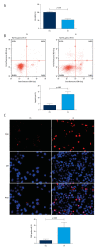
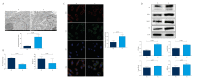
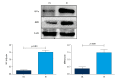
BACKGROUND As a novel pathophysiological characteristic of obstructive sleep apnea, intermittent hypoxia (IH) contributes to human renal tubular epithelial cells impairment. The underlying pathological mechanisms remain unrevealed. The present study aimed to evaluate the influence of Bcl-2 19-kDa interacting protein 3 (BNIP3)-mediated mitophagy on IH-induced renal tubular epithelial cell impairment. MATERIAL AND METHODS Human kidney proximal tubular (HK-2) cells were exposed to IH condition. IH cycles were as follows: 21% oxygen for 25 min, 21% descended to 1% for 35 min, 1% oxygen sustaining for 35 min, and 1% ascended to 21% for 25 min. The IH exposure lasted 24 h with 12 cycles of hypoxia and re-oxygenation. Both the siBNIP3 and BNIP3 vector were transfected to cells. Cell viability and apoptosis, mitochondrial morphology and function, and mitophagy were detected by cell counting kit-8, flow cytometry and TUNEL staining, transmission electron microscopy, western blotting, and immunofluorescence, respectively. RESULTS In the IH-induced HK-2 cells, inhibition of BNIP3 further aggravated mitochondrial structure damage, and decreased mitophagy level, leading to increased cell apoptosis and decreased cell viability. While overexpression of BNIP3 enhanced mitophagy, which protected mitochondrial structure, it can decrease cell death in HK-2 cells exposed to IH. CONCLUSIONS The present study showed that BNIP3-mediated mitophagy plays a protective role against IH-induced renal tubular epithelial cell impairment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
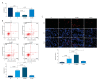
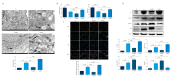
Similar articles
-
Testosterone induces renal tubular epithelial cell death through the HIF-1α/BNIP3 pathway.J Transl Med. 2019 Feb 28;17(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-1821-7. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 30819186 Free PMC article.
-
Pinocembrin ameliorates intermittent hypoxia-induced neuroinflammation through BNIP3-dependent mitophagy in a murine model of sleep apnea.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Nov 11;17(1):337. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-02014-w. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 33176803 Free PMC article.
-
HIF-1α-BNIP3-mediated mitophagy in tubular cells protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury.Redox Biol. 2020 Sep;36:101671. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101671. Epub 2020 Aug 7. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 32829253 Free PMC article.
-
Bnip3 in mitophagy: Novel insights and potential therapeutic target for diseases of secondary mitochondrial dysfunction.Clin Chim Acta. 2020 Jul;506:72-83. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.02.024. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Clin Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 32092316 Review.
-
Mitochondrial autophagy: Origins, significance, and role of BNIP3 and NIX.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Oct;1853(10 Pt B):2775-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.02.022. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25753537 Review.
Cited by
-
Retracted: Bcl-2 19-kDa Interacting Protein 3 (BNIP3)-Mediated Mitophagy Attenuates Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Human Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Injury.Med Sci Monit. 2023 Jan 31;29:e939597. doi: 10.12659/MSM.939597. Med Sci Monit. 2023. PMID: 36718665 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics Analysis and Experimental Validation of Mitochondrial Autophagy Genes in Knee Osteoarthritis.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Feb 23;17:639-650. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S444847. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 38414629 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hansrivijit P, Puthenpura MM, Ghahramani N, et al. Bidirectional association between chronic kidney disease and sleep apnea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Urol Nephrol. 2021;53:1209–22. - PubMed
-
- Lin CH, Perger E, Lyons OD. Obstructive sleep apnea and chronic kidney disease. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2018;24:549–54. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X-B, Lin Q-C, Deng C-S, et al. Elevated serum cystatin C in severe OSA younger men without complications. Sleep Breath. 2012;17:235–41. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X-B, Jiang X-T, Lin Q-C, et al. Effect of continuous positive airway pressure on serum cystatin C among obstructive sleep apnea syndrome patients. Int Urol Nephrol. 2014;46:1997–2002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

