m6A Methylation in Cardiovascular Diseases: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Potential
- PMID: 35836571
- PMCID: PMC9274458
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.908976
m6A Methylation in Cardiovascular Diseases: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
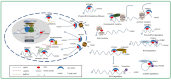
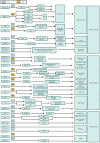
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Recent studies have shown that n6-methyladenosine (m6A) plays a major role in cardiovascular homeostasis and pathophysiology. These studies have confirmed that m6A methylation affects the pathophysiology of cardiovascular diseases by regulating cellular processes such as differentiation, proliferation, inflammation, autophagy, and apoptosis. Moreover, plenty of research has confirmed that m6A modification can delay the progression of CVD via the post-transcriptional regulation of RNA. However, there are few available summaries of m6A modification regarding CVD. In this review, we highlight advances in CVD-specific research concerning m6A modification, summarize the mechanisms underlying the involvement of m6A modification during the development of CVD, and discuss the potential of m6A modification as a therapeutic target of CVD.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; cardiovascular pathophysiology; epigenetics; m6A; m6A demethylase; m6A methyltransferase.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Xu, Liu, Chen, Liu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The critical roles of m6A modification in metabolic abnormality and cardiovascular diseases.Genes Dis. 2020 Jul 31;8(6):746-758. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2020.07.011. eCollection 2021 Nov. Genes Dis. 2020. PMID: 34522705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Roles and Mechanism of m6A Methylation in Cardiometabolic Diseases.Cells. 2022 Mar 24;11(7):1101. doi: 10.3390/cells11071101. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) in eye diseases.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Aug;48(8):6145-6150. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06596-3. Epub 2021 Jul 31. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34331665 Review.
-
N6-Methyladenosine RNA Modification in Inflammation: Roles, Mechanisms, and Applications.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 4;9:670711. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.670711. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34150765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic role of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA methylation in the cardiovascular system.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2020 Jul;21(7):509-523. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1900680. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2020. PMID: 32633106 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic signature and immune efficacy of m1A-, m5C-, m6A-, m7G-, and DNA methylation-related regulators in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cancer. 2024 Jun 11;15(13):4287-4300. doi: 10.7150/jca.95730. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38947378 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between N6-methyladenosine modification and ncRNAs in rheumatic diseases: therapeutic and diagnostic implications.Inflamm Res. 2025 May 22;74(1):79. doi: 10.1007/s00011-025-02034-3. Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40402257 Review.
-
FTO-mediated autophagy inhibition promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression by reducing the stability of SESN2 mRNA.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 7;10(5):e27571. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27571. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38495179 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying common pathways for doxorubicin and carfilzomib-induced cardiotoxicities: transcriptomic and epigenetic profiling.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 5;15(1):4395. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87442-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39910168 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular subtypes based on N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation demonstrate the heterogeneity of immune and biological functions in pediatric septic shock.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 6;9(10):e20714. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20714. eCollection 2023 Oct. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37842565 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources