Clinical Correlates and Outcomes of Dual Basiliximab and Antithymocyte Globulin Induction in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A National Study
- PMID: 35836670
- PMCID: PMC9276156
- DOI: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000001190
Clinical Correlates and Outcomes of Dual Basiliximab and Antithymocyte Globulin Induction in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A National Study
Abstract
The unplanned use of dual induction therapy with interleukin-2 receptor-blocking antibodies (IL2rAb) and antithymocyte globulin (ATG) may portend adverse outcomes.
Methods: We used national transplant registry data to study clinical correlates and outcomes of single versus dual induction therapy in adult kidney-only transplant recipients in the United States (2005-2018). The risk of death and graft loss at 1 and 5 y, according to induction therapy type, was assessed using multivariate Cox regression analysis (adjusted hazard ratio with 95% upper and lower confidence limits [LCLaHRUCL]).
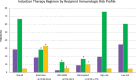
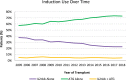
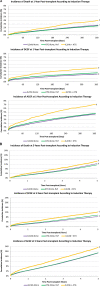
Results: Of the 157 351 recipients included in the study, 67% were treated with ATG alone, 29% were treated with IL2rAb alone, and 5% were treated with both. Compared with IL2rAb alone, the strongest correlates of dual induction included Black race, calculated panel reactive antibody ≥80%, prednisone-sparing maintenance immunosuppression, more recent transplant eras, longer cold ischemia time, and delayed graft function. Compared with ATG alone, dual induction was associated with an increased 5-y risk of death (aHR 1.071.151.23; P < 0.0001), death-censored graft failure (aHR 1.051.131.22; P < 0.05), and all-cause graft failure (aHR 1.061.121.18; P < 0.0001).
Conclusions: Further research is needed to develop risk-prediction tools to further inform optimal, individualized induction protocols for kidney transplant recipients.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Transplantation Direct. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
K.L.L. serves on the Sanofi-Genzyme speakers bureau. D.A.A. is a consultant to Sanofi-Genzyme. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Incidence, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Kidney Transplant Recipients Treated With Both Basiliximab and Antithymocyte Globulin.Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2020 Oct 15;7:2054358120964061. doi: 10.1177/2054358120964061. eCollection 2020. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 33117549 Free PMC article.
-
Immunosuppression Regimen Use and Outcomes in Older and Younger Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients: A National Registry Analysis.Transplantation. 2021 Aug 1;105(8):1840-1849. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003547. Transplantation. 2021. PMID: 33214534 Free PMC article.
-
Basiliximab: a review of its use as induction therapy in renal transplantation.Drugs. 2003;63(24):2803-35. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363240-00009. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 14664658 Review.
-
Influence of induction modality on the outcome of deceased donor kidney transplant recipients discharged on steroid-free maintenance immunosuppression.Transplantation. 2012 Apr 27;93(8):799-805. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e3182472898. Transplantation. 2012. PMID: 22290269
-
The Influence of Antithymocyte Globulin Dose on the Incidence of CMV Infection in High-risk Kidney Transplant Recipients Without Pharmacological Prophylaxis.Transplantation. 2020 Oct;104(10):2139-2147. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003124. Transplantation. 2020. PMID: 31978003
Cited by
-
Porcine anti-human lymphocyte immunoglobulin depletes the lymphocyte population to promote successful kidney transplantation.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 9;14:1124790. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1124790. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36969156 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Transplant Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the care of kidney transplant recipients. Am J Transplant. 2009;9(suppl 3):S1–S155. - PubMed
-
- Brennan DC, Daller JA, Lake KD, et al. ; Thymoglobulin Induction Study Group. Rabbit antithymocyte globulin versus basiliximab in renal transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1967–1977. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

