UBR5 promotes tumor immune evasion through enhancing IFN-γ-induced PDL1 transcription in triple negative breast cancer
- PMID: 35836797
- PMCID: PMC9274738
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.74989
UBR5 promotes tumor immune evasion through enhancing IFN-γ-induced PDL1 transcription in triple negative breast cancer
Abstract
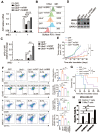
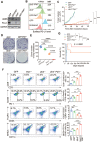
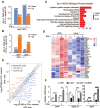
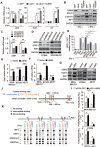
Background: The up-regulation of PD-L1 is recognized as an adaption of cancer cells to evade immune surveillance and attack. However, the intrinsic mechanisms of the induction of PD-L1 by interferon-γ (IFN-γ) in tumor microenvironment remain incompletely characterized. Ubiquitin ligase E3 component N-recognition protein 5 (UBR5) has a critical role in tumorigenesis of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) by triggering specific immune responses to the tumor. Dual targeting of UBR5 and PD-L1 exhibited superior therapeutic benefits in a preclinical TNBC model in short term. Methods: The regulation of UBR5 to PD-L1 upon IFN-γ stimulation was evaluated through in UBR5 deficiency, reconstitution or overexpression cell line models by quantitative PCR, immunohistochemistry and RNA-seq. The effects of PD-L1 regulation by UBR5 and double blockade of both genes were evaluated in mouse TNBC model. Luciferase reporter assay, chromatin immunoprecipitation-qPCR and bioinformatics analysis were performed to explore the transcription factors involved in the regulation of UBR5 to PD-L1. Results: E3 ubiquitin ligase UBR5 plays a key role in IFN-γ-induced PDL1 transcription in TNBC in an E3 ubiquitination activity-independent manner. RNA-seq-based transcriptomic analyses reveal that UBR5 globally affects the genes in the IFN-γ-induced signaling pathway. Through its poly adenylate binding (PABC) domain, UBR5 enhances the transactivation of PDL1 by upregulating protein kinase RNA-activated (PKR), and PKR's downstream factors including signal transducers and activators of transcription 1 (STAT1) and interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF1). Restoration of PD-L1 expression in UBR5-deficient tumor cells recoups their malignancy in vivo, whereas CRISPR/Cas9-mediated simultaneous abrogation of UBR5 and PD-L1 expression yields synergistic therapeutic benefits than either blockade alone, with a strong impact on the tumor microenvironment. Conclusions: This study identifies a novel regulator of PDL1 transcription, elucidates the underlying molecular mechanisms and provides a strong rationale for combination cancer immunotherapies targeting UBR5 and PD-L1.
Keywords: Interferon-γ; PD-L1; PKR/STAT1/IRF1; UBR5; triple negative breast cancer.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Histone deacetylase 2 knockout suppresses immune escape of triple-negative breast cancer cells via downregulating PD-L1 expression.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Aug 7;12(8):779. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04047-2. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34365463 Free PMC article.
-
FOXA1 enhances antitumor immunity via repressing interferon-induced PD-L1 expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.J Immunother Cancer. 2024 Nov 14;12(11):e010091. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-010091. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39542656 Free PMC article.
-
E3 Ubiquitin Ligase UBR5 Drives the Growth and Metastasis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Cancer Res. 2017 Apr 15;77(8):2090-2101. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2409. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28330927
-
Dual inhibition of STAT1 and STAT3 activation downregulates expression of PD-L1 in human breast cancer cells.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018 Jun;22(6):547-557. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2018.1471137. Epub 2018 May 2. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018. PMID: 29702007 Review.
-
A Systematic Review on the Therapeutic Potentiality of PD-L1-Inhibiting MicroRNAs for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Toward Single-Cell Sequencing-Guided Biomimetic Delivery.Genes (Basel). 2021 Aug 4;12(8):1206. doi: 10.3390/genes12081206. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34440380 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
IFI35 limits antitumor immunity in triple-negative breast cancer via CCL2 secretion.Oncogene. 2024 Mar;43(10):693-702. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02934-w. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 38216673 Free PMC article.
-
A Disulfidptosis-Related Gene Signature Associated with Prognosis and Immune Cell Infiltration in Osteosarcoma.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Sep 25;10(10):1121. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10101121. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37892851 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting "don't eat me" signal: breast cancer immunotherapy.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2025 Jun;211(2):277-292. doi: 10.1007/s10549-025-07659-w. Epub 2025 Mar 18. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2025. PMID: 40100495 Review.
-
UBR5 metabolically reprograms nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to promote glycolysis and M2 polarization via SPLUNC1 signaling.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2024 Nov 5;8(1):252. doi: 10.1038/s41698-024-00747-y. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39501021 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory mechanisms of PD-1/PD-L1 in cancers.Mol Cancer. 2024 May 18;23(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02023-w. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38762484 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

