Histone acetyltransferases CBP/p300 in tumorigenesis and CBP/p300 inhibitors as promising novel anticancer agents
- PMID: 35836809
- PMCID: PMC9274749
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.73223
Histone acetyltransferases CBP/p300 in tumorigenesis and CBP/p300 inhibitors as promising novel anticancer agents
Abstract
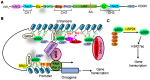
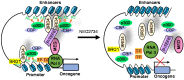
The histone acetyltransferases CBP and p300, often referred to as CBP/p300 due to their sequence homology and functional overlap and co-operation, are emerging as critical drivers of oncogenesis in the past several years. CBP/p300 induces histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) at target gene promoters, enhancers and super-enhancers, thereby activating gene transcription. While earlier studies indicate that CBP/p300 deletion/loss can promote tumorigenesis, CBP/p300 have more recently been shown to be over-expressed in cancer cells and drug-resistant cancer cells, activate oncogene transcription and induce cancer cell proliferation, survival, tumorigenesis, metastasis, immune evasion and drug-resistance. Small molecule CBP/p300 histone acetyltransferase inhibitors, bromodomain inhibitors, CBP/p300 and BET bromodomain dual inhibitors and p300 protein degraders have recently been discovered. The CBP/p300 inhibitors and degraders reduce H3K27ac, down-regulate oncogene transcription, induce cancer cell growth inhibition and cell death, activate immune response, overcome drug resistance and suppress tumor progression in vivo. In addition, CBP/p300 inhibitors enhance the anticancer efficacy of chemotherapy, radiotherapy and epigenetic anticancer agents, including BET bromodomain inhibitors; and the combination therapies exert substantial anticancer effects in mouse models of human cancers including drug-resistant cancers. Currently, two CBP/p300 inhibitors are under clinical evaluation in patients with advanced and drug-resistant solid tumors or hematological malignancies. In summary, CBP/p300 have recently been identified as critical tumorigenic drivers, and CBP/p300 inhibitors and protein degraders are emerging as promising novel anticancer agents for clinical translation.
Keywords: CBP/p300; cancer therapy; gene transcription; small molecule inhibitors; tumorigenesis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The important role of the histone acetyltransferases p300/CBP in cancer and the promising anticancer effects of p300/CBP inhibitors.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025 Jan 17;41(1):32. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09984-0. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39825161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Super-enhancers and the super-enhancer reader BRD4: tumorigenic factors and therapeutic targets.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Dec 22;9(1):470. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01775-6. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 38135679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics of anticancer activity of CBP/p300 inhibitors - Features of their classes, intracellular targets and future perspectives of their application in cancer treatment.Pharmacol Ther. 2024 May;257:108636. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2024.108636. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Pharmacol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38521246 Review.
-
Structure-activity relationship and antitumor activity of 1,4-pyrazine-containing inhibitors of histone acetyltransferases P300/CBP.Eur J Med Chem. 2022 Jul 5;237:114407. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114407. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Eur J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35512565 Free PMC article.
-
Protein lysine acetyltransferase CBP/p300: A promising target for small molecules in cancer treatment.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Feb;171:116130. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116130. Epub 2024 Jan 10. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38215693 Review.
Cited by
-
CREB-binding protein/P300 bromodomain inhibition reduces neutrophil accumulation and activates antitumor immunity in triple-negative breast cancer.JCI Insight. 2024 Sep 17;9(20):e182621. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.182621. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 39287984 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting c-Jun inhibits fatty acid oxidation to overcome tamoxifen resistance in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Oct 6;14(10):653. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06181-5. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37803002 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related promoter-switch regulates Runx1 expression in adult rat hearts.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023 Nov 7;23(1):541. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03583-3. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023. PMID: 37936072 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancers in T Cell development and malignant lesions.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Sep 17;10(1):406. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02160-7. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39284807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-hydroxybutyrate resensitizes colorectal cancer cells to oxaliplatin by suppressing H3K79 methylation in vitro and in vivo.Mol Med. 2024 Jun 23;30(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00864-1. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38910244 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vannini A, Cramer P. Conservation between the RNA polymerase I, II, and III transcription initiation machineries. Mol Cell. 2012;45:439–46. - PubMed
-
- Cramer P. Organization and regulation of gene transcription. Nature. 2019;573:45–54. - PubMed
-
- Sur I, Taipale J. The role of enhancers in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16:483–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

