Positive effect of cognitive-behavioral intervention combined with integrated health care on patients with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 35836871
- PMCID: PMC9274547
Positive effect of cognitive-behavioral intervention combined with integrated health care on patients with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Objective: This study was designed to investigate the effects of cognitive-behavioral intervention (CBI) combined with integrated health care (IHC) on glycemic control, adverse mood, health knowledge and self-efficacy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods: The clinical data of 115 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were retrospectively collected and divided into two groups according to the intervention methods, with 57 patients in group A receiving conventional care and 58 patients in group B receiving CBI combined with IHC. The blood glucose, scores of Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D), Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A), health knowledge, self-efficacy, quality of life, and nursing satisfaction were compared between the two groups before and after intervention.
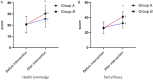
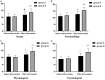
Results: Compared with group A, group B had lower glycated hemoglobin (HbAlc), 2-h postprandial glucose (2 hPG), and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels (P < 0.05), lower HAMD and HAMA scores (P < 0.05), higher health knowledge and self-efficacy scores (P < 0.05), and higher quality of life after intervention (P < 0.05). Group B exhibited a nursing satisfaction rate of 94.83%, higher than that of 70.18% in group A (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The effects of CBI combined with IHC can effectively control blood glucose and improve dysphoria, health knowledge, self-efficacy, and quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Type 2 diabetes mellitus; cognitive-behavioral intervention; dysphoria; glycemic control; health knowledge; integrated health care; self-efficacy.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of nursing based on Orem's self-care model on self-care efficacy, quality of life and adverse emotions in patients with advanced lung cancer.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Apr 15;13(4):2983-2989. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34017465 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the effectiveness of multi-disciplinary team integrated management combined with full-media health education intervention in patients with coronary heart disease and diabetes mellitus.Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2024 Nov;40(3):2745-2759. doi: 10.1080/02648725.2023.2202518. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2024. PMID: 37066841
-
A Randomized, Controlled Trial Exploring Collaborative Nursing Intervention on Self-Care Ability and Blood Glucose of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Dis Markers. 2022 Mar 22;2022:7829454. doi: 10.1155/2022/7829454. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35359881 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of high-quality nursing on blood glucose level, psychological state, and treatment compliance of patients with gestational diabetes mellitus.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Nov 15;13(11):13084-13092. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34956527 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological interventions to improve self-management of type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Jun;24(28):1-232. doi: 10.3310/hta24280. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32568666 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saslow LR, Mason AE, Kim S, Goldman V, Ploutz-Snyder R, Bayandorian H, Daubenmier J, Hecht FM, Moskowitz JT. An online intervention comparing a very low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet and lifestyle recommendations versus a plate method diet in overweight individuals with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. J Med Internet Res. 2017;19:e36. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dunlay SM, Givertz MM, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Chan M, Desai AS, Deswal A, Dickson VV, Kosiborod MN, Lekavich CL, McCoy RG, Mentz RJ, Piña IL. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and heart failure: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association and the Heart Failure Society of America: this statement does not represent an update of the 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA heart failure guideline update. Circulation. 2019;140:e294–e324. - PubMed
-
- Soderlund PD. Effectiveness of motivational interviewing for improving physical activity self-management for adults with type 2 diabetes: a review. Chronic Illn. 2018;14:54–68. - PubMed
-
- Atallah R, Côté J, Bekarian G. Evaluation of the effects of a nursing intervention on the therapeutic adherence of people with type 2 diabetes. Rech Soins Infirm. 2019;136:28–42. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
