Efficacy of anterior-posterior decompression on thoracolumbar spine fracture with spinal cord injury and analysis of risk factors for postoperative deep vein thrombosis
- PMID: 35836875
- PMCID: PMC9274601
Efficacy of anterior-posterior decompression on thoracolumbar spine fracture with spinal cord injury and analysis of risk factors for postoperative deep vein thrombosis
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the efficacy of anterior-posterior decompression on thoracolumbar spine fracture (TSF) and spinal cord injury (SCI), and assess hazard factors for postoperative deep vein thrombosis (DVT) through logistics regression.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was made on 130 patients with TSF and SCI admitted to our hospital between Jan 2018 and Jan 2020. Specifically, 72 were treated with anterior decompression (experimental group) and 58 were posterior decompression (control group). The intraoperative blood loss, procedure time, hospitalization, incision size, tactile and motor scores, injured vertebral body height, Cobb angle and complications were observed. Patients were grouped based on DVT occurrence. The risk factors were assessed through logistics regression.
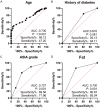
Results: In comparison to experimental group, the intraoperative blood loss, procedure time and incision size in the control group were lower (P<0.05), while the hospitalization time was shorter (P<0.05). After treatment, the tactile and motor scores were improved 3 months after operation, and the experimental group was better (P<0.05). Additionally, injured vertebral body height and Cobb angle increased, and the experimental group was higher (P<0.05). Incidence of postoperative complications revealed no marked difference (P>0.05). Logistics regression analysis manifested that ASIA rating, diabetes, obesity and age were tied to postoperative DVT.
Conclusion: Anterior decompression therapy can effectively improve the clinical outcome of patients with thoracolumbar spinal fractures and spinal cord injury on the improvement of tactile and motor functions, but posterior decompression is better than anterior surgery in terms of bleeding, incision length, operating time, and hospital stay. Surgical treatment needs to be selected according to the condition of patients. Furthermore, it was identified that ASIA rating, history of diabetes, obesity and age are risk factors affecting patients with postoperative lower extremity DVT.
Keywords: Anterior-posterior decompression; deep vein thrombosis; risk factor analysis; spinal cord injury; thoracolumbar spine fracture.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Anterior versus posterior decompression for the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures with spinal cord injury:a Meta-analysis].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2019 Mar 25;32(3):269-277. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0034.2019.03.015. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2019. PMID: 30922012 Chinese.
-
Comparison of therapeutic effects of anterior decompression and posterior decompression on thoracolumbar spine fracture complicated with spinal nerve injury.Pak J Med Sci. 2015 Mar-Apr;31(2):346-50. doi: 10.12669/pjms.312.6474. Pak J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26101488 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparative study of decompression and non-decompression surgeries in treatment of thoracolumbar fractures with intraspinal occupying and without neurological symptoms].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Aug 15;31(8):970-975. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201701101. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29806435 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Pediatric cervical kyphosis in the MRI era (1984-2008) with long-term follow up: literature review.Childs Nerv Syst. 2022 Feb;38(2):361-377. doi: 10.1007/s00381-021-05409-z. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Childs Nerv Syst. 2022. PMID: 34806157 Review.
-
Spinal neurovascular complications with anterior thoracolumbar spine surgery: a systematic review and review of thoracolumbar vascular anatomy.Neurosurg Focus. 2020 Sep;49(3):E9. doi: 10.3171/2020.6.FOCUS20373. Neurosurg Focus. 2020. PMID: 32871559
Cited by
-
Nomogram for predicting postoperative deep vein thrombosis in patients with spinal fractures caused by high-energy injuries.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024 Jan;144(1):171-177. doi: 10.1007/s00402-023-05085-5. Epub 2023 Oct 4. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024. PMID: 37792059
-
Global Prevalence of Deep Vein Thrombosis in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Neurotrauma Rep. 2025 Jun 12;6(1):491-505. doi: 10.1089/neur.2024.0144. eCollection 2025. Neurotrauma Rep. 2025. PMID: 40630647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute Translation Fracture of the Lumbar Spine With Increased Motoric Outcomes: A Case Report.Korean J Neurotrauma. 2024 Mar 14;20(1):63-68. doi: 10.13004/kjnt.2024.20.e11. eCollection 2024 Mar. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2024. PMID: 38576496 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wood KB, Li W, Lebl DR, Ploumis A. Management of thoracolumbar spine fractures. Spine J. 2014;14:145–164. - PubMed
-
- Diniz JM, Botelho RV. Is fusion necessary for thoracolumbar burst fracture treated with spinal fixation? a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2017;27:584–592. - PubMed
-
- Gavira N, Amelot A, Cook AR, Hamel A, Buffenoir K, Cristini J. Thoracolumbar spinal fracture in children: conservative or surgical treatment? Neurochirurgie. 2022;68:309–314. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
