Metronidazole-loaded nanoparticulate thermoreversible gel for gynecologic infection of Trichomonas vaginalis
- PMID: 35836901
- PMCID: PMC9274572
Metronidazole-loaded nanoparticulate thermoreversible gel for gynecologic infection of Trichomonas vaginalis
Abstract
Objective: Trichomoniasis is a common sexually-transmitted disease that is associated with increased perinatal morbidity and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) transmission. This study aimed to develop a Metronidazole-loaded nanoparticulate thermoreversible gel for gynecological infection of Trichomonas vaginalis (T. vaginalis).
Methods: The optimized nanoparticulate formulation was used in thermoreversible gel and characterized for physico-chemical properties, antiparasitic activity, and in vivo efficacy in the BALB/c mouse model.
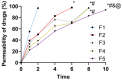
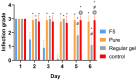
Result: A nearly threefold rise in antiparasitic activity of the optimized formulation was observed as compared to that of regular gel. Formulation F5 successfully cured the trichomoniasis within 3 days, while regular gel and pure Metronidazole (MTDZ) failed to cure this infection (P<0.05).
Conclusion: The present investigation confirms the ability of thermoreversible gel containing nanoparticulate metronidazole againstthe infection by T. vaginalis. The developed gel could be an alternative to the existing drug delivery system for the treatment of trichomoniasis.
Keywords: Metronidazole; Trichomonas vaginalis; chitosan; drug delivery; nanoparticles; poloxamer; thermoreversible; trichomoniasis; vaginal.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vulvovaginitis: screening for and management of trichomoniasis, vulvovaginal candidiasis, and bacterial vaginosis.J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2015 Mar;37(3):266-274. doi: 10.1016/S1701-2163(15)30316-9. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2015. PMID: 26001874
-
[Therapeutic aspects of trichomoniasis].Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2003 Mar-Apr;131(3-4):156-61. doi: 10.2298/sarh0304156v. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2003. PMID: 14608880 Serbian.
-
In vitro effect of octenidine dihydrochloride against Trichomonas vaginalis.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016 Mar;47(3):232-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2015.12.010. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016. PMID: 26899578
-
Drug resistance in the sexually transmitted protozoan Trichomonas vaginalis.Cell Res. 2003 Aug;13(4):239-49. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7290169. Cell Res. 2003. PMID: 12974614 Review.
-
Persistent and recurrent Trichomonas vaginalis infections: epidemiology, treatment and management considerations.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2014 Jun;12(6):673-85. doi: 10.1586/14787210.2014.887440. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2014. PMID: 24555561 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Characteristics of Vaginal Trichomoniasis Infection and Metronidazole Resistance in Vaginitis Patients.Infect Drug Resist. 2025 Feb 25;18:1161-1169. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S505326. eCollection 2025. Infect Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40027920 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced therapeutic approach for vaginal candidiasis: chitosan nanoparticulate thermoreversible in situ gels for sustained clotrimazole delivery.3 Biotech. 2025 Apr;15(4):71. doi: 10.1007/s13205-025-04240-6. Epub 2025 Mar 3. 3 Biotech. 2025. PMID: 40046956
References
-
- Fernando HV, Chan LL, Dang N, Santhanes D, Banneheke H, Nalliah S, Coombes AGA. Controlled delivery of the antiprotozoal agent (tinidazole) from intravaginal polymer matrices for treatment of the sexually transmitted infection, trichomoniasis. Pharm Dev Technol. 2019;24:348–356. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
