Crude extract of Desmodium gangeticum process anticancer activity via arresting cell cycle in G1 and modulating cell cycle-related protein expression in A549 human lung carcinoma cells
- PMID: 35836974
- PMCID: PMC9236716
- DOI: 10.37796/2211-8039.1362
Crude extract of Desmodium gangeticum process anticancer activity via arresting cell cycle in G1 and modulating cell cycle-related protein expression in A549 human lung carcinoma cells
Abstract
Background: Desmodium gangeticum (L.)DC., which belongs to the Leguminosae family, has been used in Taiwan and other subtropical countries as an external medicine to remove blood stasis, activate blood circulation, and reduce inflammation. It has been reported to have antioxidant effects and improve inflammatory responses in rats stimulated by pro-inflammatory agents and induced gastric ulcers in experimental animals over the past few decades. This plant has also been used to treat parasitic infections, but there are no reports regarding its effects on lung cancer. Therefore, this study attempted to investigate its water crude extract (in abbreviation DG) on lung cancer cells.
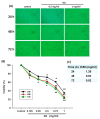
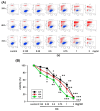
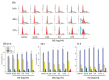
Methods: A549 human lung cancer cells were tested for survival using MTT, trypan blue, and propidium iodide. The effects of various concentrations of the crude extract of D. gangeticum (DG) (0.125~1 mg/ml) on the cell cycle and apoptosis of A549 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry and Western blotting methods.
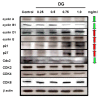
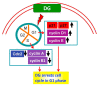
Results: DG can inhibit the growth of A549 human lung cancer cells in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. DG arrested A549 cells in the G1 phase by increasing the proteins expression of p21, p27, cyclin D1, and cyclin E. Additionally, DG decreased the expression of cyclin A, B1, and Cdc 2 (CDK1) proteins.
Conclusions: DG demonstrated the anti-lung cancer activity by arresting the cell cycle in G1 via increasing the p21, p27, cyclin D1, cyclin E, and decreasing Cdc2, cyclin A, and B1 proteins expression in A549 human lung cancer cells.
Keywords: A549 human lung cancer cells; Anti-lung cancer; Apoptosis; Cell cycle arrest; Desmodium gangeticum (L.) DC; G1.
© the Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors wish to declare no conflicts of interest on this work.
Figures

References
-
- Cause of Death Statistics. Reports from the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Taiwan. 2020. http://mohw.gov.tw/cp-5256-63399-2.html .
-
- Lung Cancer Sheet. Reports from American Lung Association. 2021. http://lung.org/lung-health-disease/lung-disease-lookup/lung-cancer/reso... .
-
- Pazdur R, Kudelka AP, Kavanagh JJ, Cohen PR, Raber MN. The taxoids: paclitaxel (Taxol) and docetaxel (Taxotere) Cancer Treat Rev. 1993;19:351–86. - PubMed
-
- Avasthi BK, Tewari JD. A preliminary phytochemical investigation of Desmodium gangeticum DC. I. J Pharmaceut Sci. 1955;44:625–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
