Association between long non-coding RNA HOTAIR polymorphism and lung cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35837044
- PMCID: PMC9257968
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2022.11477
Association between long non-coding RNA HOTAIR polymorphism and lung cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
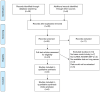
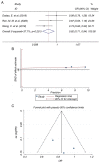
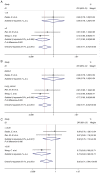
Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of long noncoding RNA (lnc)RNA has been reported to be an important factor in cancer development. Recently, lncRNA homeobox transcript antisense intergenic RNA (HOTAIR) was indicated to induce tumorigenesis of several cancer types, but the association between the SNP of lncRNA HOTAIR and lung cancer susceptibility has remained undetermined. The present meta-analysis aimed to investigate the effect of HOTAIR polymorphism on susceptibility to lung cancer. The PubMed, Ovid Medline, Embase and Cochrane Library databases were thoroughly searched. Studies containing data on the incidence of lung cancer in patients with different HOTAIR SNPs were included. The Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium was analyzed to determine genotype distribution and allele frequencies. The odds ratio (OR) was pooled to evaluate the association of different SNPs with the susceptibility to lung cancer. A total of six studies comprising 1,715 patients with lung cancer and 2,745 healthy controls were finally included. A total of 4 SNPs (rs12826786, rs1899663, rs920778 and rs4759314) were reported. Analyses for all of these SNPs individually indicated that the lncRNA HOTAIR rs1899663 C>A polymorphism was a risk factor for lung cancer (dominant mode, AA+CA vs. CC: OR=0.816, 95% CI=0.707-0.942, P=0.005). The present study was the first meta-analysis investigating the association between lncRNA HOTAIR and lung cancer susceptibility. The results indicated that the lncRNA HOTAIR rs1899663 C>A polymorphism is a risk factor for lung cancer. LncRNA HOTAIR may be of value in lung cancer screening, particularly for populations with high-risk factors, as well as prognosis prediction. Future investigations are required to further clarify the intrinsic mechanism of the role of HOTAIR in the oncogenesis of lung cancer.
Keywords: HOTAIR; SNP; lncRNA; lung cancer; susceptibility.
Copyright: © Ke et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
