Effects of 2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione on autophagy and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in human cholangiocarcinoma QBC939 cells
- PMID: 35837172
- PMCID: PMC9274070
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-22-298
Effects of 2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione on autophagy and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in human cholangiocarcinoma QBC939 cells
Abstract
Background: 2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione (DMDD) has been reported to have good antitumor effects. The aim of this study was to investigate whether DMDD induces apoptosis and autophagy in human cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) QBC939 cells and determine its effect on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.
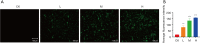
Methods: QBC939 cells were cultured in vitro and changes in cell viability were detected by the Cell Counting Kit (CCK8) assay after treatment with different concentrations of DMDD for 24, 48, and 72 h. The cells were divided into control and DMDD-treated groups (treated concentrations were 10, 15, and 20 µM/L), and the cell cycle, apoptosis, and autophagic vesicles were assessed. The expression levels of PI3K, AKT, mTOR, microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 beta (LC3-II)/I, Beclin-1, and P62 were detected by Western blot. A xenograft mouse model was constructed to detect the effect of DMDD on CCA.
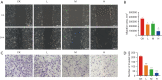
Results: The experimental results showed that DMDD was able to inhibit proliferation, migration, and invasion and induce cell cycle arrest and autophagy of QBC939 cells. In addition, DMDD decreased the protein expression of PI3K, AKT, and mTOR and increased the expression of LC3-II/I, Beclin-1, and P62. In mice, DMDD was able to inhibit the growth of tumors.
Conclusions: DMDD inhibits CCA cell viability and induces cell cycle arrest and autophagy by a mechanism that may be related to the downregulation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.
Keywords: 2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione (DMDD); PI3K/AKT/mTOR; autophagy; cholangiocarcinoma (CCA).
2022 Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jgo.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jgo-22-298/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

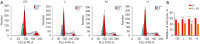


Similar articles
-
2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione mediates the effect of ROS-enhanced PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway on autophagy in breast cancer.FEBS Open Bio. 2025 Mar;15(3):474-489. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13940. Epub 2024 Dec 9. FEBS Open Bio. 2025. PMID: 39648951 Free PMC article.
-
2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione protects against MPP+-induced neurotoxicity by ameliorating oxidative stress, apoptosis and autophagy in SH-SY5Y cells.Metab Brain Dis. 2025 Jan 29;40(1):113. doi: 10.1007/s11011-025-01544-7. Metab Brain Dis. 2025. PMID: 39878879
-
Anti-Breast Cancer Effect of 2-Dodecyl-6-Methoxycyclohexa-2,5-Diene-1,4-Dione in vivo and in vitro Through MAPK Signaling Pathway.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Jul 7;14:2667-2684. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S237699. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32764871 Free PMC article.
-
2-Dodecyl-6-Methoxycyclohexa-2, 5-Diene-1, 4-Dione isolated from Averrhoa carambola L. root inhibits high glucose-induced EMT in HK-2 cells through targeting the regulation of miR-21-5p/Smad7 signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Mar;172:116280. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116280. Epub 2024 Feb 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38368837
-
Atractylodin inhibited the migration and induced autophagy in cholangiocarcinoma cells via PI3K/AKT/mTOR and p38MAPK signalling pathways.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 12;73(9):1191-1200. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgab036. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33885818
Cited by
-
2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione mediates the effect of ROS-enhanced PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway on autophagy in breast cancer.FEBS Open Bio. 2025 Mar;15(3):474-489. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13940. Epub 2024 Dec 9. FEBS Open Bio. 2025. PMID: 39648951 Free PMC article.
-
2-Dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-dien-1,4-dione alleviates liver fibrosis and improves intestinal flora and bile acid metabolism.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 16;16:1581138. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1581138. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40453659 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
