Efficacy and safety of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization-lenvatinib sequential therapy for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a single-arm clinical study
- PMID: 35837188
- PMCID: PMC9274079
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-22-525
Efficacy and safety of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization-lenvatinib sequential therapy for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a single-arm clinical study
Abstract
Background: Repeated transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) could cause ischemia of the tumor tissue and increases production of angiogenic factors in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Lenvatinib can inhibit the expression of angiogenic factors induced by ischemia after TACE and reduce angiogenesis and tumor recurrence. TACE-lenvatinib sequential therapy may improve clinical outcomes. There have been few investigations of TACE-lenvatinib sequential therapy for the treatment of unresectable HCC. We aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of TACE-lenvatinib sequential therapy for unresectable HCC.
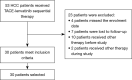
Methods: From May 2018 to May 2021, 53 consecutive patients who underwent TACE-lenvatinib sequential therapy were retrospectively reviewed. Of these, 30 patients who met the inclusion criteria were selected. Lenvatinib treatment started within 1 or 2 weeks after TACE at a dose of 8 or 12 mg once daily. Treatment response was assessed using dynamic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) according to the modified response evaluation criteria in solid tumor (mRECIST). Blood tests were also performed at every response evaluation. Patients with complete response (CR) or partial response (PR) and stable disease (SD) received continuous lenvatinib therapy, and patients with progressive disease (PD) received repeated TACE. The progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), and adverse events (AEs) were calculated. Statistical analysis was performed using the Kaplan-Meier method.
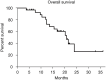
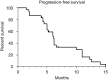
Results: The median age was 58.5±9.1 years, and 16.7% (5/30) of patients were female. A total of 12 patients were categorized as Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) Stage B and 18 were BCLC Stage C. The mean follow-up time was 15.7 months. The ORR was 76.7% (23/30), and the DCR was 96.7% (29/30). The median PFS was 6.1 months, and the median OS was 20.7 months. The most common lenvatinib-related AE was rash, and the most common TACE-related AE was elevated aspartate aminotransferase (AST). No treatment-related mortality was observed.
Conclusions: From our findings, TACE-lenvatinib sequential therapy may prolong OS and PFS in patients with unresectable HCC, and the side effects are acceptable. The efficacy and safety of the sequential therapy should be confirmed in multiple center randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with a large sample and sufficient follow-up period.
Keywords: Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE); hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); lenvatinib; sequential therapy; unresectable.
2022 Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jgo.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jgo-22-525/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization-lenvatinib sequential therapy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: a retrospective study.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Apr;13(2):780-786. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-239. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35557575 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of PD-1 inhibitor combined with TACE in the first-line treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.Med Oncol. 2024 Mar 25;41(5):91. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02309-5. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38526607
-
The impact of PD-1 inhibitors on prognosis in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated with TACE and lenvatinib: a retrospective study.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 21;14(1):14334. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63571-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38906915 Free PMC article.
-
Lenvatinib for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Literature Review.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Jan 6;14(1):36. doi: 10.3390/ph14010036. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33418941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization combined with lenvatinib and PD-1 inhibitor in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Pharmacol Ther. 2024 May;257:108634. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2024.108634. Epub 2024 Mar 16. Pharmacol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38499069 Review.
Cited by
-
Safety and efficacy of DEB-TACE in combination with lenvatinib and camrelizumab for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC): a two-centre retrospective study.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 22;15:1422784. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1422784. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39502690 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety analysis of selective hepatic vein occlusion combined with arterial chemoembolization versus conventional transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Apr 30;15(2):710-720. doi: 10.21037/jgo-23-992. Epub 2024 Apr 18. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38756643 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of treatment based on TKIs in combination with PD-1 inhibitors for unresectable recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Surg Oncol. 2023 Feb 18;21(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12957-023-02939-5. World J Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36803872 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
