Expression characteristics of long non-coding RNA in colon adenocarcinoma and its potential value for judging the survival and prognosis of patients: bioinformatics analysis based on The Cancer Genome Atlas database
- PMID: 35837189
- PMCID: PMC9274031
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-22-384
Expression characteristics of long non-coding RNA in colon adenocarcinoma and its potential value for judging the survival and prognosis of patients: bioinformatics analysis based on The Cancer Genome Atlas database
Abstract
Background: To investigate the expression characteristics of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) in colon adenocarcinoma (COAD) and its potential value in predicting the prognosis of patient survival.
Methods: We downloaded COAD-related RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) data and patient survival data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). The data were analyzed for lncRNA expression differences, subjected to Cox regression analysis for survival rate, and Kaplan-Meier (KM) survival curves were plotted to analyze the role of the key genes related to prognostic survival by pathway enrichment analysis.
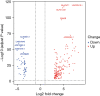
Results: The data of 494 COAD clinical samples from TCGA were analyzed; 204 lncRNAs were differentially expressed, 156 were up-regulated, and 48 were down-regulated. The 10 genes with the most significant expression differences were Linc02418, Blacat1, ELFN1-AS1, CRNDE, AC002384.1, AL353801.1, LINC01645, AC073283.2, AC087379.1, and LINC00484. Cox regression analysis of 204 lncRNA genes showed that 23 lncRNA genes with significant effects on the prognosis and survival rate of COAD patients were obtained when P<0.05 was used as the threshold. With P≤0.001 as the threshold, the KM curves of 4 genes (Linc02257, Linc02474, Ac010789.1, Ac083967.1) were statistically significant (P<0.05). The gene Linc02257 was selected for Gene Ontology (GO) function and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis, and it was revealed that the inheritance of Linc02257-regulated gene expression was closely related to tumor development, such as collagen-containing extracellular matrix, organogenesis, activity of membrane protein receptors, and ion channel activity. The signaling pathways regulated by Linc02257 were also closely related to tumors, such as neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway, calcium signaling pathway, and protein digestion and absorption.
Conclusions: In COAD, lncRNA is differentially expressed and plays an important role in the disease regulation. It has potential application value in the diagnosis, targeted therapy, and prognosis of COAD patients.
Keywords: Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA); The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA); bioinformatics analysis; colon cancer.
2022 Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jgo.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jgo-22-384/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The Interferon Gamma-Related Long Noncoding RNA Signature Predicts Prognosis and Indicates Immune Microenvironment Infiltration in Colon Adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 7;12:876660. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.876660. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35747790 Free PMC article.
-
LINC02257, an Enhancer RNA of Prognostic Value in Colon Adenocarcinoma, Correlates With Multi-Omics Immunotherapy-Related Analysis in 33 Cancers.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Apr 30;8:646786. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.646786. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33996902 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of differential expression profiles of mRNAs and lncRNAs and identification of a 14-lncRNA prognostic signature for patients with colon adenocarcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2018 May;39(5):2365-2375. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6324. Epub 2018 Mar 19. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29565464
-
Analysis of lncRNA-Associated ceRNA Network Reveals Potential lncRNA Biomarkers in Human Colon Adenocarcinoma.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(5):1778-1791. doi: 10.1159/000493623. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30231249
-
A novel m7G-related lncRNA risk model for predicting prognosis and evaluating the tumor immune microenvironment in colon carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 4;12:934928. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.934928. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35992788 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Uncovering Alterations in Cancer Epigenetics via Trans-Dimensional Markov Chain Monte Carlo and Hidden Markov Models.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 15:2023.06.15.545168. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.15.545168. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 37398181 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Potential Role of the Intratumoral Microbiota in Prognosis of Head and Neck Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 22;24(20):15456. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015456. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895136 Free PMC article.
-
A cuproptosis-related lncRNAs signature predicts prognosis and reveals pivotal interactions between immune cells in colon cancer.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 14;10(14):e34586. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34586. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39114018 Free PMC article.
-
LINC02418 suppresses endometrial cancer progression via regulating miR-494-3p/RASGRF1 axis.J Mol Histol. 2025 Jan 22;56(1):72. doi: 10.1007/s10735-024-10327-w. J Mol Histol. 2025. PMID: 39841298
-
Cuproptosis: the mechanisms of copper-induced cell death and its implication in colorectal cancer.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 May 21. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04263-z. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40397118 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
