Resveratrol inhibits the proliferation, invasion, and migration, and induces the apoptosis of human gastric cancer cells through the MALAT1/miR-383-5p/DDIT4 signaling pathway
- PMID: 35837196
- PMCID: PMC9274040
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-22-307
Resveratrol inhibits the proliferation, invasion, and migration, and induces the apoptosis of human gastric cancer cells through the MALAT1/miR-383-5p/DDIT4 signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: We aimed to study the effects and potential mechanism of resveratrol (RS) in gastric cancer (GC).
Methods: The human GC cell line SGC7901 was treated with different concentrations of RS (0, 1, 5 µM) for 24 hours. The messenger ribonucleic acid or protein expressions levels of metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1), micro ribonucleic acid-383-5p (miR-383-5p), and DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 (DDIT4) in GC cells were determined by Western blot and quantitative real-time polymerase chain assays. Cells were then transfected with miR-383-5p inhibitor (inhibitor), inhibitor negative control (NC), MALAT1-interfering RNA (si-MALAT1), si-DDIT4 and negative interference control (si-NC). The Cell Counting Kit-8 method, scratch assay, and transwell assay were performed to evaluate cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Additionally, flow cytometry was used to examine apoptosis, and the target relationship was examined by a luciferase-reporter gene analysis.
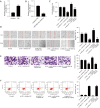
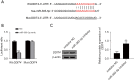
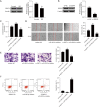
Results: RS treatment downregulated the expression of MALAT1, repressed cell proliferation, inhibited cell migration and invasion (all P<0.05), and induced apoptosis (P<0.05) in GC cells. When the cells were treated with RS and inhibited the expression of MALAT1 meanwhile, the above anti-cancer effects were more significant (all P<0.05). Target prediction and the luciferase-reporter gene analysis showed that MALAT1 targeted miR-383-5p (P<0.05). When suppressing the expression of MALAT1 and miR-383-5p, the anti-cancer effects caused by the silencing of MALAT1 were absent (all P<0.05). We also found that miR-383-5p targeted DDIT4 protein. When the expression of miR-383-5p and DDIT4 in the GC cells was inhibited, the promoting cancer effects caused by the inhibition of miR-383-5p were reversed (all P<0.05).
Conclusions: This study found that RS inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion of human GC cells through the metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1)/miR-383-5p/DDIT4 pathway and induced apoptosis.
Keywords: MALAT1/miR-383-5p/DDIT4 pathway; Resveratrol; gastric cancer cell.
2022 Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Both authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jgo.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jgo-22-307/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion via miR-374b-5p/SRSF7 axis in non-small cell lung cancer.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Feb;24(4):1853-1862. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202002_20363. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32141554
-
si-MALAT1 attenuates thymic cancer cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis via the miR-145-5p/HMGA2 pathway.Oncol Lett. 2021 Aug;22(2):585. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12846. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 34122636 Free PMC article.
-
Long Noncoding RNA MALAT1 Knockdown Inhibits Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion and Promotes Apoptosis in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells Through Regulating miR-515-3p/TRIM65 Axis.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020 Dec 31. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2020.3730. Online ahead of print. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020. PMID: 33395541
-
Long Non-Coding RNA Metastasis Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 (MALAT1) Promotes Hypertension by Modulating the Hsa-miR-124-3p/Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 3, Group C, Member 2 (NR3C2) and Hsa-miR-135a-5p/NR3C2 Axis.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Mar 29;26:e920478. doi: 10.12659/MSM.920478. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32222724 Free PMC article.
-
A review of the mechanism of DDIT4 serve as a mitochondrial related protein in tumor regulation.Sci Prog. 2021 Jan-Mar;104(1):36850421997273. doi: 10.1177/0036850421997273. Sci Prog. 2021. PMID: 33729069 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anticancer effects of SH003 and its active component Cucurbitacin D on oral cancer cell lines via modulation of EMT and cell viability.Oncol Res. 2025 Apr 18;33(5):1217-1227. doi: 10.32604/or.2025.059791. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 40296905 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA MALAT-1: A versatile regulator in cancer progression, metastasis, immunity, and therapeutic resistance.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Feb 1;9(2):388-406. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.01.015. eCollection 2024 Jun. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 38511067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitory Potential of Resveratrol in Cancer Metastasis: From Biology to Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2023 May 14;15(10):2758. doi: 10.3390/cancers15102758. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37345095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of a miRNA Panel for Differentiating Lung Adenocarcinoma Brain Metastases and Glioblastoma.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Feb 8;17(4):581. doi: 10.3390/cancers17040581. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40002176 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Biological Strategies for Melanoma Therapy: A Focus on lncRNAs and Their Targeting.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Apr 9;17(8):1273. doi: 10.3390/cancers17081273. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40282449 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
