Efficacy and safety of sequential therapy with sorafenib and regorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a two-center study in China
- PMID: 35837206
- PMCID: PMC9274072
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-22-397
Efficacy and safety of sequential therapy with sorafenib and regorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a two-center study in China
Abstract
Background: Regorafenib is a standard 2nd-line treatment for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but the efficacy and safety of sequential therapy with sorafenib and regorafenib among advanced HCC patients in China is not clear.
Methods: This was a retrospective, two-center, cohort study of advanced HCC patients who received sequential therapy of sorafenib and regorafenib from October 2018 to April 2020 at 2 Chinese institutions. The patients were converted directly to regorafenib after failing to respond to sorafenib monotherapy. The patients underwent evaluations every 4-6 weeks to determine the efficacy and safety of the treatment according to physiological, laboratory, and radiological results. A radiological evaluation using computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging scans was conducted. The outcomes included overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS).
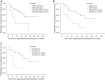
Results: A total of 43 patients received regorafenib as a 2nd-line treatment after sorafenib progression. Of these patients, 26 (60.5%) and 17 (39.5%) were diagnosed with Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stages B and C, respectively. The median PFS was 11.0 [95% confidence interval (CI): 5.8-16.2] months, and the median OS was 17.0 (95% CI: 12.8-21.2) months. Conversely, the most common toxicities were hand-foot skin reaction (48.8%), diarrhea (32.6%), and hypertension (14%). The most common grade 3-4 toxicities were hypoalbuminemia (4.7%), anemia (4.7%), and thrombocytopenia (4.7%). Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) ≥400, alanine transaminase (ALT) ≥60 IU/L, and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) ≥60 IU/L before 2nd-line treatment were associated with PFS in the univariable analyses. The Cox proportional-hazards regression analysis showed that AFP [hazard ratio (HR) =0.225; 95% CI: 0.073-0.688; P=0.009], ALT (HR =0.195; 95% CI: 0.051-0.741; P=0.016), AST (HR =0.209; 95% CI: 0.063-0.697; P=0.011), and presence of extrahepatic metastasis (HR =0.074; 95% CI: 0.009-0.608; P=0.015) before 2nd-line treatment were independently associated with PFS.
Conclusions: The sequential therapy of sorafenib and regorafenib is well-tolerated and effective in advanced HCC patients after sorafenib progression based on our two-center real-world data. Patients with good liver function reserve and a high level of AFP before 2nd-line treatment may benefit from sequential treatment. These results still need further validation.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); RESORCE; regorafenib; sequential therapy; sorafenib.
2022 Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jgo.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jgo-22-397/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative Efficacy of Cabozantinib and Regorafenib for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Adv Ther. 2020 Jun;37(6):2678-2695. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01378-y. Epub 2020 May 18. Adv Ther. 2020. PMID: 32424805 Free PMC article.
-
On-Treatment Albumin-Bilirubin Grade: Predictor of Response and Outcome of Sorafenib-Regorafenib Sequential Therapy in Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 26;13(15):3758. doi: 10.3390/cancers13153758. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34359658 Free PMC article.
-
Real-Life Experience of Regorafenib in Patients With Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 6;13:917384. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.917384. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35734398 Free PMC article.
-
Regorafenib compared to nivolumab after sorafenib failure in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2023 Aug;32(8):839-845. doi: 10.17219/acem/158488. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 37140014
-
Regorafenib: A Review in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Drugs. 2018 Jun;78(9):951-958. doi: 10.1007/s40265-018-0932-4. Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29915898 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Beyond the Border of Advanced Stage Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 27;16(11):2034. doi: 10.3390/cancers16112034. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors approved for systemic therapy of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: recent advances and future perspectives.Discov Oncol. 2024 Jul 3;15(1):259. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01110-0. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38960980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Baseline Albumin-Bilirubin grade as a predictor of response and outcome of regorafenib therapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2023 Oct 19;23(1):1006. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11488-9. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37858207 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
