SR-DSFF and FENet-ReID: A Two-Stage Approach for Cross Resolution Person Re-Identification
- PMID: 35837221
- PMCID: PMC9276474
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4398727
SR-DSFF and FENet-ReID: A Two-Stage Approach for Cross Resolution Person Re-Identification
Abstract
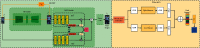
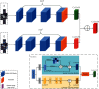
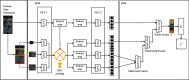
In real-life scenarios, the accuracy of person re-identification (Re-ID) is subject to the limitation of camera hardware conditions and the change of image resolution caused by factors such as camera focusing errors. People call this problem cross-resolution person Re-ID. In this paper, we improve the recognition accuracy of cross-resolution person Re-ID by enhancing the image enhancement network and feature extraction network. Specifically, we treat cross-resolution person Re-ID as a two-stage task: the first stage is the image enhancement stage, and we propose a Super-Resolution Dual-Stream Feature Fusion sub-network, named SR-DSFF, which contains SR module and DSFF module. The SR-DSFF utilizes the SR module recovers the resolution of the low-resolution (LR) images and then obtains the feature maps of the LR images and super-resolution (SR) images, respectively, through the dual-stream feature fusion with learned weights extracts and fuses feature maps from LR and SR images in the DSFF module. At the end of SR-DSFF, we set a transposed convolution to visualize the feature maps into images. The second stage is the feature acquisition stage. We design a global-local feature extraction network guided by human pose estimation, named FENet-ReID. The FENet-ReID obtains the final features through multistage feature extraction and multiscale feature fusion for the Re-ID task. The two stages complement each other, making the final pedestrian feature representation has the advantage of accurate identification compared with other methods. Experimental results show that our method improves significantly compared with some state-of-the-art methods.
Copyright © 2022 Zongzong Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Wang Y., Wang L., You Y., et al. Resource Aware Person Re-identification across Multiple Resolutions. Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; June 2018; Salt Lake City, UT, USA. pp. 8042–8051. - DOI
-
- Huang Y., Zha Z.-J., Fu X., Zhang W. Illumination-invariant Person Re-identification. Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia (MM’19); October 2019; Nice, France. pp. 365–373. - DOI
-
- Hou R., Ma B., Chang H., Gu X., Shan S., Chen X. Vrstc: Occlusion-free Video Person Re-identification. Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR); June 2019; Long Beach, CA, USA. pp. 7183–7192. - DOI
-
- Pang J., Zhang D., Li H., Liu W., Yu Z. Hazy Re-ID: An Interference Suppression Model for Domain Adaptation Person Re-identification under Inclement Weather Condition. Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME); July 2021; Shenzhen, China. - DOI
-
- Zheng L., Shen L., Lu T., Wang S., Wang J., Tian Q. Scalable Person Re-identification: A Benchmark. Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV); December 2015; Santiago, Chile. IEEE; - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

