The Impact of Timing of Pertussis Vaccination During Pregnancy on Infant Antibody Levels at Birth: A Multi-Country Analysis
- PMID: 35837400
- PMCID: PMC9273881
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.913922
The Impact of Timing of Pertussis Vaccination During Pregnancy on Infant Antibody Levels at Birth: A Multi-Country Analysis
Abstract
Background: Pertussis vaccination during pregnancy is an effective strategy at reducing pertussis-related morbidity and mortality in infancy and is recommended across several countries. However, the optimal timepoint for vaccination in pregnancy to afford maximal protection to newborns is yet to be elucidated. This multi-country analysis aimed to model the impact of timing of vaccination during pregnancy on infant antibody titers at birth.
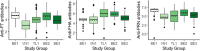
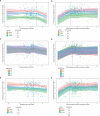
Methods: A multi-country analysis on a cohort of mother-infant pairs (n=698) vaccinated between 19.6-37.1 weeks gestation was conducted. Data taken from four parent studies on pertussis vaccination during pregnancy were modelled using natural cubic splines and linear mixed models to study the association of both gestational age at vaccination and the interval between vaccination and delivery with pertussis-specific cord blood antibody levels after pertussis vaccination during pregnancy.
Results: Term born infants on average achieve the highest antibody levels at birth if women are vaccinated before 31 weeks' gestation. When considering both term and preterm deliveries, an interval of at least 7.5 weeks between vaccination and delivery is required to achieve the highest cord blood antibody levels. The models show that vaccinating earlier than these timeframes will also provide the infant with equally high antibody levels at birth.
Conclusions: Vaccinating in the second and early third trimester results in the highest antibody levels at birth. Vaccinating earlier within this window is needed to provide equal benefits to both term and preterm born infants.
Keywords: Tdap; multi-country analysis; pregnancy; timing; vaccination.
Copyright © 2022 Gomme, Wanlapakorn, Ha, Leuridan, Herzog and Maertens.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global Health Observatory (GHO) Data: Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis (DTP3) Immunization Coverage. Available at: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/immunization.
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Vaccine-Preventable Diseases: Monitoring System. 2020 Global Summary. (2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

