KRAS mutations as essential promoters of lymphangiogenesis via extracellular vesicles in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 35838046
- PMCID: PMC9282924
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI161454
KRAS mutations as essential promoters of lymphangiogenesis via extracellular vesicles in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
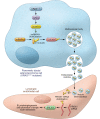
Kirsten rat sarcoma virus (KRAS) gene mutations are present in more than 90% of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDACs). KRASG12D is the most frequent alteration, promoting preneoplastic lesions and associating with a more aggressive phenotype. These tumors possess increased intratumoral lymphatic networks and frequent lymph node (LN) metastases. In this issue of the JCI, Luo, Li, et al. explored the relationship between the presence of the KRASG12D mutation and lymphangiogenesis in PDAC. The authors used in vitro and in vivo models and an elegant mechanistic approach to describe an alternative pathway for lymphangiogenesis promotion. KRASG12D induced SUMOylation of heterogenous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 (hnRNPA1) via SAE1 and SUMO2 activation. SUMOylated hnRNPA1 was loaded into extracellular vesicles (EVs) and internalized by human endothelial lymphatic cells (HLEC). Further, SUMOylated hnRNPA1 promoted lymphangiogenesis and LN metastasis by stabilizing prospero homeodomain protein 1 (PROX1) mRNA. These data provide mechanistic insight into cancer lymphangiogenesis with the potential for developing biomarkers and RAS pathway therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment on
-
KRAS mutant-driven SUMOylation controls extracellular vesicle transmission to trigger lymphangiogenesis in pancreatic cancer.J Clin Invest. 2022 Jul 15;132(14):e157644. doi: 10.1172/JCI157644. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 35579947 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

