Newborn screening for neurodevelopmental diseases: Are we there yet?
- PMID: 35838066
- PMCID: PMC9796120
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31988
Newborn screening for neurodevelopmental diseases: Are we there yet?
Abstract
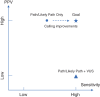
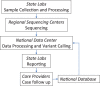
In the US, newborn screening (NBS) is a unique health program that supports health equity and screens virtually every baby after birth, and has brought timely treatments to babies since the 1960's. With the decreasing cost of sequencing and the improving methods to interpret genetic data, there is an opportunity to add DNA sequencing as a screening method to facilitate the identification of babies with treatable conditions that cannot be identified in any other scalable way, including highly penetrant genetic neurodevelopmental disorders (NDD). However, the lack of effective dietary or drug-based treatments has made it nearly impossible to consider NDDs in the current NBS framework, yet it is anticipated that any treatment will be maximally effective if started early. Hence there is a critical need for large scale pilot studies to assess if and how NDDs can be effectively screened at birth, if parents desire that information, and what impact early diagnosis may have. Here we attempt to provide an overview of the recent advances in NDD treatments, explore the possible framework of setting up a pilot study to genetically screen for NDDs, highlight key technical, practical, and ethical considerations and challenges, and examine the policy and health system implications.
© 2022 The Authors. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part C: Seminars in Medical Genetics published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

