Hippocampal dentate gyrus integrity revealed with ultrahigh resolution diffusion imaging predicts memory performance in older adults
- PMID: 35838075
- PMCID: PMC10510739
- DOI: 10.1002/hipo.23456
Hippocampal dentate gyrus integrity revealed with ultrahigh resolution diffusion imaging predicts memory performance in older adults
Abstract
Medial temporal lobe (MTL) atrophy is a core feature of age-related cognitive decline and Alzheimer's disease (AD). While regional volumes and thickness are often used as a proxy for neurodegeneration, they lack the sensitivity to serve as an accurate diagnostic test and indicate advanced neurodegeneration. Here, we used a submillimeter resolution diffusion weighted MRI sequence (ZOOMit) to quantify microstructural properties of hippocampal subfields in older adults (63-98 years old) using tensor derived measures: fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD). We demonstrate that the high-resolution sequence, and not a standard resolution sequence, identifies dissociable profiles for CA1, dentate gyrus (DG), and the collateral sulcus. Using ZOOMit, we show that advanced age is associated with increased MD of the CA1 and DG as well as decreased FA of the DG. Increased MD of the DG, reflecting decreased cellular density, mediated the relationship between age and word list recall. Further, increased MD in the DG, but not DG volume, was linked to worse spatial pattern separation. Our results demonstrate that ultrahigh-resolution diffusion imaging enables the detection of microstructural differences in hippocampal subfield integrity and will lead to novel insights into the mechanisms of age-related memory loss.
Keywords: aging; dentate gyrus; hippocampus; magnetic resonance imaging; memory.
© 2022 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures


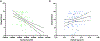
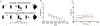
Similar articles
-
A protocol for manual segmentation of medial temporal lobe subregions in 7 Tesla MRI.Neuroimage Clin. 2017 May 26;15:466-482. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2017.05.022. eCollection 2017. Neuroimage Clin. 2017. PMID: 28652965 Free PMC article.
-
Memory impairment in Amyloidβ-status Alzheimer's disease is associated with a reduction in CA1 and dentate gyrus volume: In vivo MRI at 7T.Neuroimage. 2024 Apr 15;292:120607. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2024.120607. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Neuroimage. 2024. PMID: 38614372
-
Evaluation of Cognitive Deficits and Structural Hippocampal Damage in Encephalitis With Leucine-Rich, Glioma-Inactivated 1 Antibodies.JAMA Neurol. 2017 Jan 1;74(1):50-59. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.4226. JAMA Neurol. 2017. PMID: 27893017
-
Acute cycling exercise and hippocampal subfield function and microstructure in healthy older adults.Hippocampus. 2023 Oct;33(10):1123-1138. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23571. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Hippocampus. 2023. PMID: 37526119 Free PMC article.
-
Structural magnetic resonance imaging for the early diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease in people with mild cognitive impairment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 2;3(3):CD009628. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009628.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32119112 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Circulating PACAP levels are associated with altered imaging measures of entorhinal cortex neurite density in posttraumatic stress disorder.Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2024;15(1):2335793. doi: 10.1080/20008066.2024.2335793. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2024. PMID: 38590134 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution multi-shot diffusion imaging of structural networks in healthy neurocognitive aging.Neuroimage. 2023 Jul 15;275:120191. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.120191. Epub 2023 May 25. Neuroimage. 2023. PMID: 37244322 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

