Hanging drop sample preparation improves sensitivity of spatial proteomics
- PMID: 35838077
- PMCID: PMC9320080
- DOI: 10.1039/d2lc00384h
Hanging drop sample preparation improves sensitivity of spatial proteomics
Abstract
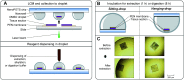
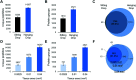
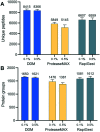
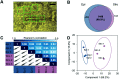
Spatial proteomics holds great promise for revealing tissue heterogeneity in both physiological and pathological conditions. However, one significant limitation of most spatial proteomics workflows is the requirement of large sample amounts that blurs cell-type-specific or microstructure-specific information. In this study, we developed an improved sample preparation approach for spatial proteomics and integrated it with our previously-established laser capture microdissection (LCM) and microfluidics sample processing platform. Specifically, we developed a hanging drop (HD) method to improve the sample recovery by positioning a nanowell chip upside-down during protein extraction and tryptic digestion steps. Compared with the commonly-used sitting-drop method, the HD method keeps the tissue pixel away from the container surface, and thus improves the accessibility of the extraction/digestion buffer to the tissue sample. The HD method can increase the MS signal by 7 fold, leading to a 66% increase in the number of identified proteins. An average of 721, 1489, and 2521 proteins can be quantitatively profiled from laser-dissected 10 μm-thick mouse liver tissue pixels with areas of 0.0025, 0.01, and 0.04 mm2, respectively. The improved system was further validated in the study of cell-type-specific proteomes of mouse uterine tissues.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

