Postoperative radiotherapy in pIIIA-N2 non-small cell lung cancer after complete resection and adjuvant chemotherapy: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 35839025
- PMCID: PMC11132350
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029550
Postoperative radiotherapy in pIIIA-N2 non-small cell lung cancer after complete resection and adjuvant chemotherapy: A meta-analysis
Abstract
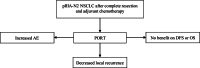
Background: This study aimed to evaluate the effect of postoperative radiotherapy (PORT) in patients with pIIIA-N2 non-small cell lung cancer after complete resection and adjuvant chemotherapy.
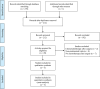
Methods: Electronic databases (PubMed, Web of Science databases, Embase, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials) were systematically searched to extract randomized control trials comparing PORT with observation in pIIIA-N2 non-small cell lung cancer patients until October 2021. Main outcomes were disease-free survival (DFS), overall survival (OS), and local recurrence.
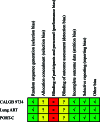
Results: Three-phase 3 randomized control trials involving 902 patients were included: 455 patients in the PORT group and 447 patients in the observation group. The methodological quality of the 3 randomized control trials were high quality. The pooled analysis revealed that PORT decreased local recurrence rate (odds ratio = 0.56, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.40-0.76). However, PORT did not improve median DFS (hazard ratio = 0.84, 95% CI: 0.71-1.00) and OS (hazard ratio = 1.02, 95% CI: 0.68-1.52).
Conclusions: PORT decreased the incidence of local recurrence. However, PORT did not improve DFS and OS.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
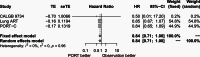


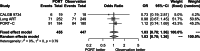
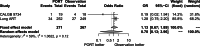
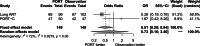
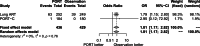
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. . Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Goldstraw P, Chansky K, Crowley J, et al. . The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals for revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (eighth) edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11:39–51. - PubMed
-
- Douillard JY, Rosell R, De Lena M, et al. . Adjuvant vinorelbine plus cisplatin versus observation in patients with completely resected stage IB-IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer (Adjuvant Navelbine International Trialist Association [ANITA]): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7:719–27. - PubMed
-
- Arriagada R, Bergman B, Dunant A, et al. . Cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:351–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

