A guide to regional analgesia for Total Knee Arthroplasty
- PMID: 35839095
- PMCID: PMC8693230
- DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.6.210045
A guide to regional analgesia for Total Knee Arthroplasty
Abstract
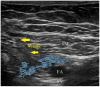
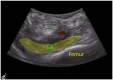
Regional analgesia has been introduced successfully into the postoperative pain management after total knee arthroplasty, reducing pain scores, opioid use and adverse effects. Combination of regional analgesia techniques is associated with better pain management and lower side effects than single regional techniques. Adductor canal block provides good analgesia and considerably lower detrimental effect in muscular strength than femoral nerve block, enhancing surgical recovery. Infiltration techniques may have equivalent analgesic effect than epidural analgesia and peripheral nerve blocks, however there should be awareness of dose dependent toxicity. Novel long-acting local anesthetics role for regional analgesia is still to be determined, and will require larger randomized trials to support its advantage over traditional local anesthetics.
© 2021 The author(s) 2021
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Price AJ, Alvand A, Troelsen A, et al. Knee replacement. Lancet. 2018;392:1672-1682. - PubMed
-
- Inacio MCS, Paxton EW, Graves SE, Namba RS, Nemes S. Projected increase in total knee arthroplasty in the United States - an alternative projection model. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25:1797-1803. - PubMed
-
- Siddiqi A, Warren JA, McLaughlin J, et al. Demographic, Comorbidity, and Episode-of-Care Differences in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg [Am]. 2021;103-A:227-234. - PubMed
-
- Cleveland Clinic OME Arthroplasty Group. Understanding the main predictors of length of stay after total hip arthroplasty: patient-related or procedure-related risk factors? J Arthroplasty. 2021;36:1663-1670.e4 - PubMed
-
- Anis HK, Strnad GJ, Klika AK, Zajichek A, Spindler KP, Barsoum WK, Higuera CA, Piuzzi NS. Developing a personalized outcome prediction tool for knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]. 2020;102-B:1183-1193. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

