Epigenetic regulator genes direct lineage switching in MLL/AF4 leukemia
- PMID: 35839448
- PMCID: PMC10488321
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2021015036
Epigenetic regulator genes direct lineage switching in MLL/AF4 leukemia
Abstract
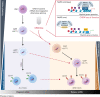
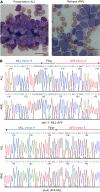
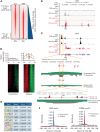
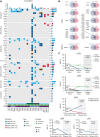
The fusion gene MLL/AF4 defines a high-risk subtype of pro-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Relapse can be associated with a lineage switch from acute lymphoblastic to acute myeloid leukemia, resulting in poor clinical outcomes caused by resistance to chemotherapies and immunotherapies. In this study, the myeloid relapses shared oncogene fusion breakpoints with their matched lymphoid presentations and originated from various differentiation stages from immature progenitors through to committed B-cell precursors. Lineage switching is linked to substantial changes in chromatin accessibility and rewiring of transcriptional programs, including alternative splicing. These findings indicate that the execution and maintenance of lymphoid lineage differentiation is impaired. The relapsed myeloid phenotype is recurrently associated with the altered expression, splicing, or mutation of chromatin modifiers, including CHD4 coding for the ATPase/helicase of the nucleosome remodelling and deacetylation complex. Perturbation of CHD4 alone or in combination with other mutated epigenetic modifiers induces myeloid gene expression in MLL/AF4+ cell models, indicating that lineage switching in MLL/AF4 leukemia is driven and maintained by disrupted epigenetic regulation.
© 2022 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Comment in
-
KMT2A-rearranged leukemia: the shapeshifter.Blood. 2022 Oct 27;140(17):1833-1835. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022017645. Blood. 2022. PMID: 36301633 No abstract available.
References
-
- Moorman AV, Ensor HM, Richards SM, et al. Prognostic effect of chromosomal abnormalities in childhood B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: results from the UK Medical Research Council ALL97/99 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(5):429–438. - PubMed
-
- Germano G, Pigazzi M, del Giudice L, et al. Two consecutive immunophenotypic switches in a child with MLL-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 2006;91(5 suppl):ECR09. - PubMed
-
- Jiang JG, Roman E, Nandula SV, Murty VV, Bhagat G, Alobeid B. Congenital MLL-positive B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) switched lineage at relapse to acute myelocytic leukemia (AML) with persistent t(4;11) and t(1;6) translocations and JH gene rearrangement. Leuk Lymphoma. 2005;46(8):1223–1227. - PubMed
-
- Rossi JG, Bernasconi AR, Alonso CN, et al. Lineage switch in childhood acute leukemia: an unusual event with poor outcome. Am J Hematol. 2012;87(9):890–897. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NC/P002412/1/NC3RS_/National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research/United Kingdom
- 23389/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- NC/V001639/1/NC3RS_/National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research/United Kingdom
- G0802259/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/S021590/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

