Epidemiological characteristics and disease burden of infectious mononucleosis in hospitalized children in China: A nationwide retrospective study
- PMID: 35840103
- PMCID: PMC9583177
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virs.2022.07.007
Epidemiological characteristics and disease burden of infectious mononucleosis in hospitalized children in China: A nationwide retrospective study
Abstract
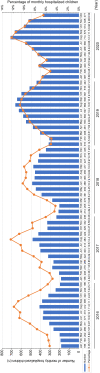
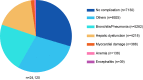
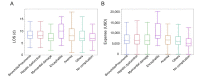
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is very common, with the infection rate in adults over 90% worldwide. Infectious mononucleosis (IM) is caused by primary infection with EBV. Most IM patients are generally considered to have a favorable prognosis, but a few patients will also develop complications. Children with severe symptoms will require hospitalization. However, the disease burden of children hospitalized with IM in China has been rarely described. In this study, we included the Face sheets of discharge medical records from 27 member children's hospitals of Futang Research Center of Pediatric Development from Jan 1st, 2016 to Dec 31st, 2020, and medical information such as gender, age, region, time of admission, length of stay and expenditure were extracted. There were 24,120 IM cases, which accounted for 0.42% (24,120/5,693,262) of all hospitalized cases during this period. The ratio of male to female was 1.48:1. Hospitalization for IM in the 4-6 years age group was the highest among inpatients of all age groups. Case numbers increased year by year between 2016 and 2020, and the monthly hospitalization was generally high from Jul to Sep but reduced from Jan to Feb per year. Bronchitis/pneumonia and hepatic dysfunction were two common complications in hospitalized IM patients. The median length of stay was 8 days, and the median cost of hospitalization was 970.59 US dollars. This study will help understand the epidemiological characteristics and disease burden of hospitalized children with IM in China.
Keywords: Children; Disease burden; Epidemiological characteristics; Epstein-Barr virus (EBV); Infectious mononucleosis (IM).
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chabay P.A., Preciado M.V. EBV primary infection in childhood and its relation to B-cell lymphoma development: a mini-review from a developing region. Int. J. Cancer. 2013;133:1286–1292. - PubMed
-
- Chan C.W., Chiang A.K., Chan K.H., Lau A.S. Epstein-Barr virus-associated infectious mononucleosis in Chinese children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2003;22:974–978. - PubMed
-
- Chinn I.K., Eckstein O.S., Peckham-Gregory E.C., Goldberg B.R., Forbes L.R., Nicholas S.K., Mace E.M., Vogel T.P., Abhyankar H.A., Diaz M.I., Heslop H.E., Krance R.A., Martinez C.A., Nguyen T.C., Bashir D.A., Goldman J.R., Stray-Pedersen A., Pedroza L.A., Poli M.C., Aldave-Becerra J.C., McGhee S.A., Al-Herz W., Chamdin A., Coban-Akdemir Z.H., Jhangiani S.N., Muzny D.M., Cao T.N., Hong D.N., Gibbs R.A., Lupski J.R., Orange J.S., McClain K.L., Allen C.E. Genetic and mechanistic diversity in pediatric hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood. 2018;132:89–100. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

