Assessment of inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis using thermography and machine learning: a fast and automated technique
- PMID: 35840312
- PMCID: PMC9295660
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002458
Assessment of inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis using thermography and machine learning: a fast and automated technique
Abstract
Objectives: Sensitive detection of joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is crucial to the success of the treat-to-target strategy. In this study, we characterise a novel machine learning-based computational method to automatically assess joint inflammation in RA using thermography of the hands, a fast and non-invasive imaging technique.
Methods: We recruited 595 patients with arthritis and osteoarthritis, as well as healthy subjects at two hospitals over 4 years. Machine learning was used to assess joint inflammation from the thermal images of the hands using ultrasound as the reference standard, obtaining a Thermographic Joint Inflammation Score (ThermoJIS). The machine learning model was trained and tuned using data from 449 participants with different types of arthritis, osteoarthritis or without rheumatic disease (development set). The performance of the method was evaluated based on 146 patients with RA (validation set) using Spearman's rank correlation coefficient, area under the receiver-operating curve (AUROC), average precision, sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive value and F1-score.
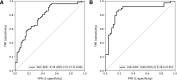
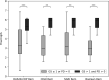
Results: ThermoJIS correlated moderately with ultrasound scores (grey-scale synovial hypertrophy=0.49, p<0.001; and power Doppler=0.51, p<0.001). The AUROC for ThermoJIS for detecting active synovitis was 0.78 (95% CI, 0.71 to 0.86; p<0.001). In patients with RA in clinical remission, ThermoJIS values were significantly higher when active synovitis was detected by ultrasound.
Conclusions: ThermoJIS was able to detect joint inflammation in patients with RA, even in those in clinical remission. These results open an opportunity to develop new tools for routine detection of joint inflammation.
Keywords: arthritis, rheumatoid; inflammation; synovitis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: IM-I and MAM-L are cofounders and shareholders of Singularity Biomed. Singularity Biomed has filed a patent application for the computational method.
Figures


Similar articles
-
External Validation of the Machine Learning-Based Thermographic Indices for Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Prospective Longitudinal Study.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jun 30;14(13):1394. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14131394. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001284 Free PMC article.
-
A Thermographic Disease Activity Index for remote assessment of rheumatoid arthritis.RMD Open. 2022 Nov;8(2):e002615. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002615. RMD Open. 2022. PMID: 36410775 Free PMC article.
-
Thermographic and ultrasound assessment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: can thermography detect subclinical synovitis at the wrist?BMC Rheumatol. 2024 Nov 19;8(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s41927-024-00435-1. BMC Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39558420 Free PMC article.
-
Sonographic synovial vascularity of synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014 Apr;53(4):586-91. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ket311. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014. PMID: 24049097 Review.
-
Ultrasonography for diagnosis, monitoring and treatment of tenosynovitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Dan Med J. 2018 Mar;65(3):B5474. Dan Med J. 2018. PMID: 29510818 Review.
Cited by
-
Microwave Radiometry for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Inflammatory Arthritis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Feb 7;13(4):609. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13040609. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36832097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Large language models and rheumatology: are we there yet?Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2024 Sep 18;9(2):rkae119. doi: 10.1093/rap/rkae119. eCollection 2025. Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2024. PMID: 40256630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
External Validation of the Machine Learning-Based Thermographic Indices for Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Prospective Longitudinal Study.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jun 30;14(13):1394. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14131394. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001284 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Ultrasound Power Doppler Synovitis at Clinically Quiescent Joints and Thermographic Joint Inflammation Assessment in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Oct 25;14(21):2384. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14212384. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39518352 Free PMC article.
-
[Application and prospects of infrared thermography in rheumatic diseases].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Dec 18;56(6):1132-1136. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.06.031. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 39690783 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
