MRTF specifies a muscle-like contractile module in Porifera
- PMID: 35840552
- PMCID: PMC9287330
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-31756-9
MRTF specifies a muscle-like contractile module in Porifera
Abstract
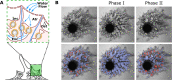
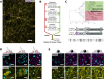
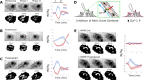
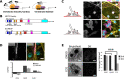
Muscle-based movement is a hallmark of animal biology, but the evolutionary origins of myocytes are unknown. Although believed to lack muscles, sponges (Porifera) are capable of coordinated whole-body contractions that purge debris from internal water canals. This behavior has been observed for decades, but their contractile tissues remain uncharacterized with respect to their ultrastructure, regulation, and development. We examine the sponge Ephydatia muelleri and find tissue-wide organization of a contractile module composed of actin, striated-muscle myosin II, and transgelin, and that contractions are regulated by the release of internal Ca2+ stores upstream of the myosin-light-chain-kinase (MLCK) pathway. The development of this contractile module appears to involve myocardin-related transcription factor (MRTF) as part of an environmentally inducible transcriptional complex that also functions in muscle development, plasticity, and regeneration. As an actin-regulated force-sensor, MRTF-activity offers a mechanism for how the contractile tissues that line water canals can dynamically remodel in response to flow and can re-form normally from stem-cells in the absence of the intrinsic spatial cues typical of animal embryogenesis. We conclude that the contractile module of sponge tissues shares elements of homology with contractile tissues in other animals, including muscles, indicating descent from a common, multifunctional tissue in the animal stem-lineage.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

