The Medical Segmentation Decathlon
- PMID: 35840566
- PMCID: PMC9287542
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30695-9
The Medical Segmentation Decathlon
Abstract
International challenges have become the de facto standard for comparative assessment of image analysis algorithms. Although segmentation is the most widely investigated medical image processing task, the various challenges have been organized to focus only on specific clinical tasks. We organized the Medical Segmentation Decathlon (MSD)-a biomedical image analysis challenge, in which algorithms compete in a multitude of both tasks and modalities to investigate the hypothesis that a method capable of performing well on multiple tasks will generalize well to a previously unseen task and potentially outperform a custom-designed solution. MSD results confirmed this hypothesis, moreover, MSD winner continued generalizing well to a wide range of other clinical problems for the next two years. Three main conclusions can be drawn from this study: (1) state-of-the-art image segmentation algorithms generalize well when retrained on unseen tasks; (2) consistent algorithmic performance across multiple tasks is a strong surrogate of algorithmic generalizability; (3) the training of accurate AI segmentation models is now commoditized to scientists that are not versed in AI model training.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No funding contributed explicitly to the organization and running of the challenge. The challenge award has been kindly provided by NVIDIA. However, NVIDIA did not influence the design or running of the challenge as they were not part of the organizing committee. R.M.S. received royalties from iCAD, Philips, ScanMed, Translation Holdings, and PingAn. Individually funding sourcing unrelated to the challenge has been listed in the Acknowledgments section. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

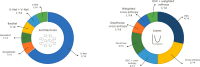
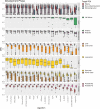
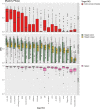
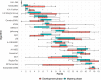
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

