Accurate image-based CSF volume calculation of the lateral ventricles
- PMID: 35840587
- PMCID: PMC9287564
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-15995-w
Accurate image-based CSF volume calculation of the lateral ventricles
Abstract
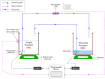
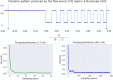
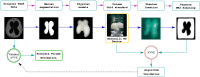
The size/volume of the brain's ventricles is essential in diagnosing and treating many neurological disorders, with various forms of hydrocephalus being some of the most common. Initial ventricular size and changes, if any, in response to disease progression or therapeutic intervention are monitored by serial imaging methods. Significant variance in ventricular size is readily noted, but small incremental changes can be challenging to appreciate. We have previously reported using artificial intelligence to determine ventricular volume. The values obtained were compared with those calculated using the inaccurate manual segmentation as the "gold standard". This document introduces a strategy to measure ventricular volumes where manual segmentation is not employed to validate the estimations. Instead, we created 3D printed models that mimic the lateral ventricles and measured those 3D models' volume with a tuned water displacement device. The 3D models are placed in a gel and taken to the magnetic resonance scanner. Images extracted from the phantoms are fed to an artificial intelligence-based algorithm. The volumes yielded by the automation must equal those yielded by water displacement to assert validation. Then, we provide certified volumes for subjects in the age range (1-114) months old and two hydrocephalus patients.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Eliminating the need for manual segmentation to determine size and volume from MRI. A proof of concept on segmenting the lateral ventricles.PLoS One. 2023 May 11;18(5):e0285414. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0285414. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37167315 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence for automatic cerebral ventricle segmentation and volume calculation: a clinical tool for the evaluation of pediatric hydrocephalus.J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2020 Dec 1;27(2):131-138. doi: 10.3171/2020.6.PEDS20251. Print 2021 Feb 1. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 33260138 Free PMC article.
-
Automated Lateral Ventricular and Cranial Vault Volume Measurements in 13,851 Patients Using Deep Learning Algorithms.World Neurosurg. 2021 Apr;148:e363-e373. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2020.12.148. Epub 2021 Jan 6. World Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 33421645
-
Volume estimation of brain ventricles using Cavalieri's principle and Atlas-based methods in Alzheimer disease: Consistency between methods.J Clin Neurosci. 2020 Aug;78:333-338. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2020.04.092. Epub 2020 Apr 29. J Clin Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32360163
-
Congenital obstruction of foramen of Monro: report of 10 patients and literature review.Childs Nerv Syst. 2018 Apr;34(4):707-715. doi: 10.1007/s00381-017-3671-z. Epub 2017 Dec 5. Childs Nerv Syst. 2018. PMID: 29209884 Review.
Cited by
-
Automatic measurement and reference values setting of intracranial cerebrospinal fluid volume: a large-scale analysis of computed tomography images.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025 Jul 1;15(7):6185-6199. doi: 10.21037/qims-2024-2571. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 40727365 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gerhardt P, Frommhold W. Atlas of Anatomic Correlations in CT and MRI. Thieme; 1988.
-
- Swinburne Nathaniel, C., Bansal Anmol, G., Amit, A., & Doshi Amish, H. Neuroimaging in central nervous system infections. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. . 10.1007/s11910-017-0756-8 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Tumani, H., Huss, A. & Bachhuber, F. Chapter 2—The cerebrospinal fluid and barriers-anatomic and physiologic considerations. in Cerebrospinal Fluid in Neurologic Disorders. Vol. 146. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. 21–32. (Deisenhammer, F., Teunissen, C.E. & Tumani, H. eds.). 10.1016/B978-0-12-804279-3.00002-2 (Elsevier, 2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

