E2F4 transcription factor is a prognostic biomarker related to immune infiltration of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 35840663
- PMCID: PMC9287548
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-16541-4
E2F4 transcription factor is a prognostic biomarker related to immune infiltration of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
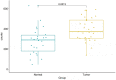
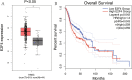
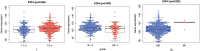
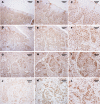
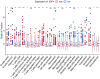
To investigate the relationship between the transcription factor, E2F4, and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), and to preliminarily explore the signaling pathways and immunological role of E2F4. The mRNA expression of E2F4 in HNSCC was evaluated by searching Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) datasets. E2F4 protein expression was analyzed by immunohistochemistry using the CMU1h-ENT database. The association between E2F4 expression and tumor infiltration of immune cells was analyzed. Intracellular signaling by E2F4 was explored using KEGG and GO analysis. The correlation of E2F4 expression with clinical characteristics and its prognostic role were validated and analyzed in TCGA database. From the analysis of GEO and TCGA data, E2F4 expression was found to be up-regulated in HNSCC tumor tissues, and its level was associated with T, Grade, and M staging. Kaplan-Meier curve and Cox analyses indicated that the high expression of E2F4 was related to a poor prognosis. Thus, E2F4 was considered a potential prognostic factor for HNSCC. Immunohistochemical staining showed that E2F4 was mainly localized in the cell nucleus; it was highly expressed in HNSCC tissues, with a significant difference noted from that in pericancerous mucosa tissues. A correlation was observed between the differential expression of E2F4 and the immune infiltration of HNSCC. As revealed by KEGG and GO analysis, differential enrichment was found in the cell cycle, spliceosome, meiosis, microbial polysaccharide synthesis, and WNT signaling pathway, as well as in cyclic adenosine monophosphate, ERBB2, VEGF, GCNP and MYC pathways. E2F4 plays an important role in tumor progression and may be a critical biological prognostic factor for HNSCC. In addition, it functions in the nucleus as a transcription factor, regulates immune cells, and could be a promising molecular target for the diagnosis and treatment of HNSCC.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
High Expression of E2F4 Is an Adverse Prognostic Factor and Related to Immune Infiltration in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Dec 15;2022:4731364. doi: 10.1155/2022/4731364. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36567912 Free PMC article.
-
CTHRC1 is a prognostic biomarker correlated with immune infiltration in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Jun 27;24(1):742. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04525-x. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38937712 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of TPD52L2 in HNSCC: prognostic significance and correlation with immune infiltrates.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Oct 7;24(1):1191. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04977-1. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39375696 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive review regarding the association of E2Fs with the prognosis and immune infiltrates in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Asian J Surg. 2024 May;47(5):2106-2121. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2024.01.130. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Asian J Surg. 2024. PMID: 38320907 Review.
-
Somatostatin receptor2 (SSTR2) expression, prognostic implications, modifications and potential therapeutic strategies associates with head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2024 Jan;193:104223. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2023.104223. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38036157 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription Factor E2F4 Promote Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Gastric Cancer Cells by transcriptionally activating DSCC1.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Sep 16;20(12):4978-4998. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.99590. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39309429 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Analysis of HPV-Positive Oesophageal Tissue Reveals Upregulation of Genes Linked to Cell Cycle and DNA Replication.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 24;26(1):56. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010056. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39795915 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

