Characterizing cis-regulatory elements using single-cell epigenomics
- PMID: 35840754
- PMCID: PMC9771884
- DOI: 10.1038/s41576-022-00509-1
Characterizing cis-regulatory elements using single-cell epigenomics
Abstract
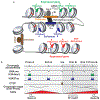
Cell type-specific gene expression patterns and dynamics during development or in disease are controlled by cis-regulatory elements (CREs), such as promoters and enhancers. Distinct classes of CREs can be characterized by their epigenomic features, including DNA methylation, chromatin accessibility, combinations of histone modifications and conformation of local chromatin. Tremendous progress has been made in cataloguing CREs in the human genome using bulk transcriptomic and epigenomic methods. However, single-cell epigenomic and multi-omic technologies have the potential to provide deeper insight into cell type-specific gene regulatory programmes as well as into how they change during development, in response to environmental cues and through disease pathogenesis. Here, we highlight recent advances in single-cell epigenomic methods and analytical tools and discuss their readiness for human tissue profiling.
© 2022. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
B.R. is a shareholder and consultant of Arima Genomics, Inc., and a co-founder of Epigenome Technologies, Inc. K.J.G. is a consultant of Genentech and a shareholder in Vertex Pharmaceuticals and Neurocrine Biosciences. These relationships have been disclosed to and approved by the UCSD Independent Review Committee.
Figures

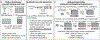

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RF1 MH128838/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG067153/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK122607/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG009402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG069107/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 MH124612/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH121282/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG066018/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH114828/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG012059/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 DK105554/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK114650/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD102534/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK120429/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 DK107977/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL148867/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA052769/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK105554/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AG073198/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG011585/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG003151/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 MH114831/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 MH130994/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY030591/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AG079758/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 MH114830/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY031663/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

