Effects of high-fat diet on thyroid autoimmunity in the female rat
- PMID: 35840950
- PMCID: PMC9287994
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-022-01093-5
Effects of high-fat diet on thyroid autoimmunity in the female rat
Abstract
Background: While contributions of dyslipidemia to autoimmune diseases have been described, its impact on thyroid autoimmunity (TA) is less clear. Programmed cell death 1(PD-1)/PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1) immune checkpoint is crucial in preventing autoimmune attack while its blockade exacerbates TA. We thus unveiled the effect of high-fat diet (HFD) on TA, focusing on the contribution of PD-1/PD-L1.
Methods: Female Sprague Dawley (SD) rats were randomly fed with a regular diet or HFD (60% calories from fat) for 24 weeks. Then, thyroid ultrasonography was performed and samples were collected for lipid and thyroid-related parameter measure.
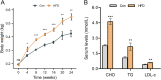
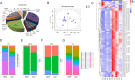
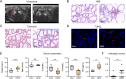
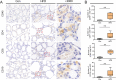
Results: HFD rats exhibited hyperlipemia and abnormal biosynthesis of the unsaturated fatty acid in serum detected by lipidomics. These rats displayed a relatively lower echogenicity and increased inflammatory infiltration in thyroid accompanied by rising serum thyroid autoantibody levels and hypothyroidism, mimicking human Hashimoto's thyroiditis. These alterations were concurrent with decreased mRNA and immunostaining of intrathyroidal PD-1 and also serum PD-1 levels but not the PD-L1 expression, suggesting a role of a PD-1 pathway. Meanwhile, the infiltration of B and T cell, a key cellular event inhibited by the PD-1 signals, was enhanced in the thyroid of HFD rats, along with thyroid fibrosis and apoptosis.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that HFD triggers TA through a mechanism possibly involving downregulation of PD-1-related immunosuppression, providing a novel insight into the link between dyslipidemia and autoimmune toxicities.
Keywords: High-fat diet; Lymphocytic infiltration; PD-1; PD-L1; Thyroid autoimmunity.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ott J, Meusel M, Schultheis A, Promberger R, Pallikunnel SJ, Neuhold N, et al. The incidence of lymphocytic thyroid infiltration and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis increased in patients operated for benign goiter over a 31-year period. Virchows Arch. 2011;459:277–81. doi: 10.1007/s00428-011-1130-x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

