Exosomal miR-132-3p from mesenchymal stromal cells improves synaptic dysfunction and cognitive decline in vascular dementia
- PMID: 35841005
- PMCID: PMC9284820
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-022-02995-w
Exosomal miR-132-3p from mesenchymal stromal cells improves synaptic dysfunction and cognitive decline in vascular dementia
Abstract
Background/aims: Vascular dementia (VD) results in cognition and memory deficit. Exosomes and their carried microRNAs (miRs) contribute to the neuroprotective effects of mesenchymal stromal cells, and miR-132-3p plays a key role in neuron plasticity. Here, we investigated the role and underlying mechanism of MSC EX and their miR-132-3p cargo in rescuing cognition and memory deficit in VD mice.
Methods: Bilateral carotid artery occlusion was used to generate a VD mouse model. MiR-132-3p and MSC EX levels in the hippocampus and cortex were measured. At 24-h post-VD induction, mice were administered with MSC EX infected with control lentivirus (EXCon), pre-miR-132-3p-expressing lentivirus (EXmiR-132-3p), or miR-132-3p antago lentivirus (EXantagomiR-132-3p) intravenously. Behavioral and cognitive tests were performed, and the mice were killed in 21 days after VD. The effects of MSC EX on neuron number, synaptic plasticity, dendritic spine density, and Aβ and p-Tau levels in the hippocampus and cortex were determined. The effects of MSC EX on oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD)-injured neurons with respect to apoptosis, and neurite elongation and branching were determined. Finally, the expression levels of Ras, phosphorylation of Akt, GSK-3β, and Tau were also measured.
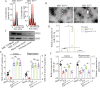
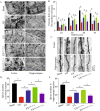
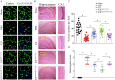
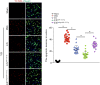
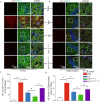
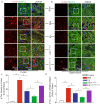
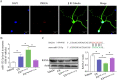
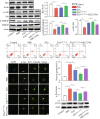
Results: Compared with normal mice, VD mice exhibited significantly decreased miR-132-3p and MSC EX levels in the cortex and hippocampus. Compared with EXCon treatment, the infusion of EXmiR-132-3p was more effective at improving cognitive function and increasing miR-132-3p level, neuron number, synaptic plasticity, and dendritic spine density, while decreasing Aβ and p-Tau levels in the cortex and hippocampus of VD mice. Conversely, EXantagomiR-132-3p treatment significantly decreased miR-132-3p expression in cortex and hippocampus, as well as attenuated EXmiR-132-3p treatment-induced functional improvement. In vitro, EXmiR-132-3p treatment inhibited RASA1 protein expression, but increased Ras and the phosphorylation of Akt and GSK-3β, and decreased p-Tau levels in primary neurons by delivering miR-132-3p, which resulted in reduced apoptosis, and increased neurite elongation and branching in OGD-injured neurons.
Conclusions: Our studies suggest that miR-132-3p cluster-enriched MSC EX promotes the recovery of cognitive function by improving neuronal and synaptic dysfunction through activation of the Ras/Akt/GSK-3β pathway induced by downregulation of RASA1.
Keywords: Exosomes; Mesenchymal stromal cells; Synaptic plasticity; Vascular dementia; miR-132-3p.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Yang Y, Xu HY, Deng QW, Wu GH, Zeng X, Jin H, et al. Electroacupuncture facilitates the integration of a grafted TrkC-modified mesenchymal stem cell-derived neural network into transected spinal cord in rats via increasing neurotrophin-3. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021;27:776–791. doi: 10.1111/cns.13638. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

