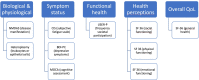
A conceptual disease model for quality of life in mitochondrial disease
- PMID: 35841006
- PMCID: PMC9287990
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-022-02411-9
A conceptual disease model for quality of life in mitochondrial disease
Abstract
Background: Previous studies in patients with a mitochondrial disease (MD) highlight the high prevalence of cognitive impairments, fatigue, depression, and a lower quality of life (QoL). The relationship with biological and physiological factors remains complex. The aim of this study is to investigate the status of and interrelationships between biological and physiological functioning, cognitive functioning as well as fatigue, depression, societal participation, health perceptions, and QoL, by using the Wilson and Cleary conceptual disease model, adapted to MD.
Methods: Patients with a genetically confirmed MD were included. The following health concepts in MD were investigated according to the conceptual model: (1) Biological and physiological: disease manifestation (Newcastle Mitochondrial Disease Adult Scale), (2) Symptom status: cognitive functioning, patient reported fatigue and depressive symptoms, (3) Functional health: societal participation, (4) Patient reported health perceptions, and (5) Overall QoL. Data were compared to healthy normative data and/or data from other patient groups. Correlations as well as a hierarchical regression analysis were performed to assess the relations between the different levels of health concepts in the conceptual model.
Results: Of the 95 included patients, 42% had a severe disease manifestation. Comparable or worse than normative data and other patient groups, 35% reported cognitive impairments, 80% severe fatigue, and 27% depressive symptoms. Patients experienced impairments in societal participation and QoL. Disease manifestation was significantly correlated with cognitive functioning, societal participation, physical functioning and overall QoL, but not with fatigue or depressive symptoms. Almost all outcome measures regarding functional health, health perceptions and QoL were correlated with symptom status variables. Overall QoL was significantly predicted by fatigue and physical functioning.
Conclusions: Symptom status is related to the functional health, health perceptions and QoL in patients with MD. Moreover, fatigue and physical functioning are important contributors to the overall QoL of MD patients. In order to provide adequate patient care it is important to have a broad view on patients' functioning, not only by providing a proper clinical assessment, but also to screen for symptom status; cognitive functioning, fatigue and depression.
Keywords: Cognitive functioning; Depressive symptoms; Disease manifestation; Fatigue; Mental health; Mitochondrial disease; Quality of life; Societal participation; Wilson and Cleary model.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cognitive functioning and mental health in children with a primary mitochondrial disease.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022 Oct 1;17(1):368. doi: 10.1186/s13023-022-02510-7. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022. PMID: 36183138 Free PMC article.
-
A descriptive analysis of quality of life using patient-reported measures in major depressive disorder in a naturalistic outpatient setting.Qual Life Res. 2013 Apr;22(3):585-96. doi: 10.1007/s11136-012-0187-6. Epub 2012 Apr 29. Qual Life Res. 2013. PMID: 22544416
-
Factors predicting quality of life and societal participation after survival of a cardiac arrest: A prognostic longitudinal cohort study.Resuscitation. 2018 Feb;123:51-57. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2017.11.069. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Resuscitation. 2018. PMID: 29223603
-
How non-functioning pituitary adenomas can affect health-related quality of life: a conceptual model and literature review.Pituitary. 2018 Apr;21(2):208-216. doi: 10.1007/s11102-017-0860-4. Pituitary. 2018. PMID: 29302835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct Wound Healing and Quality-of-Life Outcomes in Subgroups of Patients With Venous Leg Ulcers With Different Symptom Cluster Experiences.J Pain Symptom Manage. 2017 May;53(5):871-879. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2016.12.336. Epub 2017 Jan 4. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2017. PMID: 28063868 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and Safety of Photobiomodulation in MELAS: Protocol for a Series of N-of-1 Trials.J Clin Med. 2025 Mar 17;14(6):2047. doi: 10.3390/jcm14062047. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40142856 Free PMC article.
-
The profound implications of mitochondrial myopathy on activities of daily living: an observational qualitative study of standardized structured and semi-structured patient interviews.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2025 Jul 25;16:20406223251344763. doi: 10.1177/20406223251344763. eCollection 2025. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2025. PMID: 40735368 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beck AT, Steer RA, Brown GK. Beck depression inventory-II. Amsterdam: Pearson Assessment and Information; 2002.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical